Features

2026 Renewable Energy Outlook: A Potentially Quieter Year, But Steady Growth to Continue
While most experts anticipate a potentially quieter 2026 for the renewable energy industry, new capacity deployment is expected to continue growing, primarily driven by China. This will ultimately seal the fate of coal power, further accelerating its decline. Still, more ambitious and urgent action is needed to achieve a triple increase in renewable energy capacity by 2030.

COP30 Outcomes: Takeaways from the UN Climate Talks in Brazil
COP30 ended with some significant wins for climate action. Adaptation finance was increased, new funding was gathered for renewable energy, and a 1.5°C goal was reaffirmed. However, the lack of a plan for a global phase out of fossil fuels soured the final COP30 text. This dichotomy defines this year's COP and highlights the lack of continuity in critical aspects of global climate action.
Renewable Energy
Best Renewable Energy Stocks to Buy in 2026
Renewable energy equities are shifting from policy-driven bets to market-driven growth in 2026, with major players delivering contracted cash flows, scalable platforms and AI-powered demand. From NextEra and Brookfield Renewable to solar manufacturers like First Solar and innovators like Nextpower, the sector now blends defensive stability with upside growth as data centres and electrification accelerate demand. This market migration could redefine core portfolios as clean-energy fundamentals align with a multipronged growth thesis.

Best Renewable Energy Companies To Invest In 2026
Investors are shifting capital towards renewable energy as AI, data centres and global electrification drive unprecedented electricity demand. With global renewable investment now surpassing oil and gas by hundreds of billions, companies offering scale, technology and stable cash flows are poised to lead in 2026.
Fossil Fuel

Proposed Ammonia Co-firing Solutions More Expensive than Renewables
The LCOE for ammonia co-firing exceeds that of renewable electricity, rendering Southeast Asia’s plans economically unfeasible. According to experts, instead of exposing themselves to the financial, environmental and health risks associated with ammonia co-firing, ASEAN nations should prioritise the accelerated deployment of renewable energy.

Gas Turbine Shortage in Vietnam and the Philippines
Experts note that delays, exacerbated by global gas turbine shortages, and regulatory and bankability challenges are giving clear market signals to move away from gas projects and scale up renewables and battery storage deployments instead.
Region
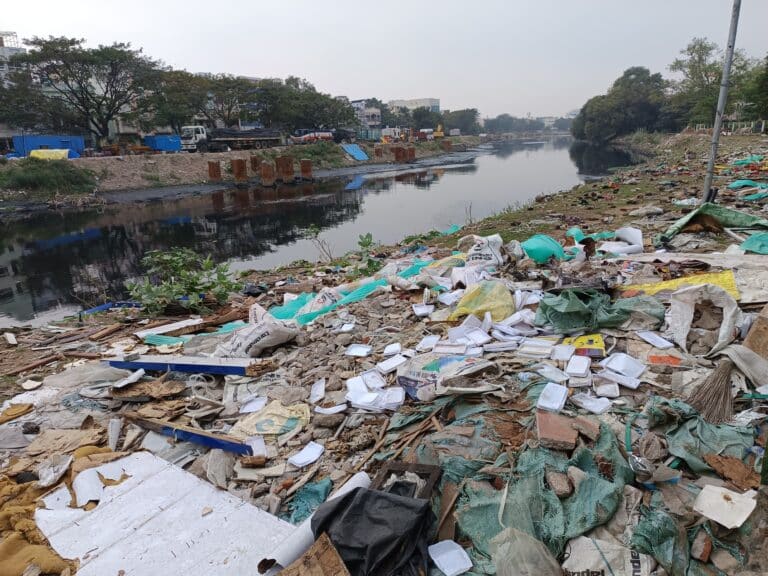

The Most Polluted River in India Is Not the Ganga or Yamuna
India’s river pollution crisis has a new face: the Cooum in Chennai, now considered the country’s most polluted waterway. Across 46% of India’s rivers, contamination from untreated sewage, industrial discharges and waste is threatening public health, livelihoods and ecosystems, with major stretches, such as the Yamuna and Sabarmati, illustrating the depth of the challenge. The drivers, impacts and the urgent policy gaps must be addressed to reverse decades of neglect.
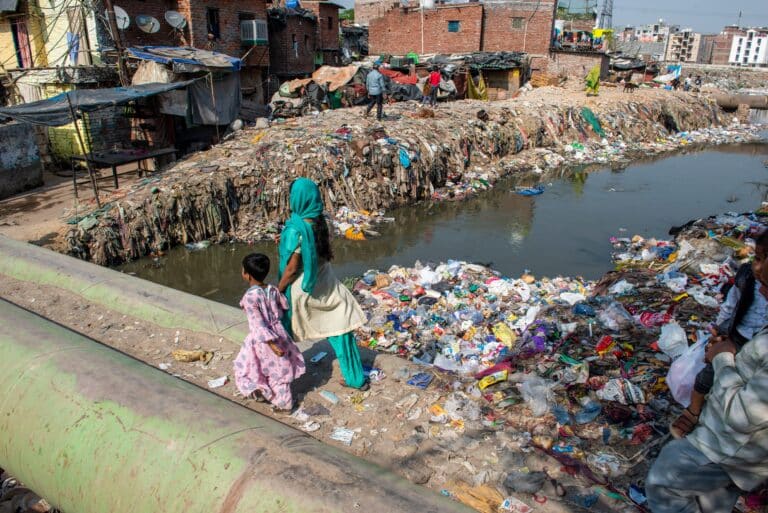

Water Pollution in India and Its Toll on Rivers and People
Water pollution in India remains an urgent crisis, threatening public health, ecosystems and the economy despite ongoing cleanup efforts. With 40% of monitored river stretches failing to meet basic water-quality norms and groundwater contamination on the rise, urgent, coordinated action is needed to safeguard the country’s scarce freshwater resources.