Is “Greenflation” behind Higher Global Energy Prices?
Source: The Economist
05 April 2022 – by Eric Koons
Globally, energy prices are reaching new highs. Is this the result of greenflation? To understand if this constitutes greenflation, it is important to first understand what it is.
What is Greenflation or Green Inflation?
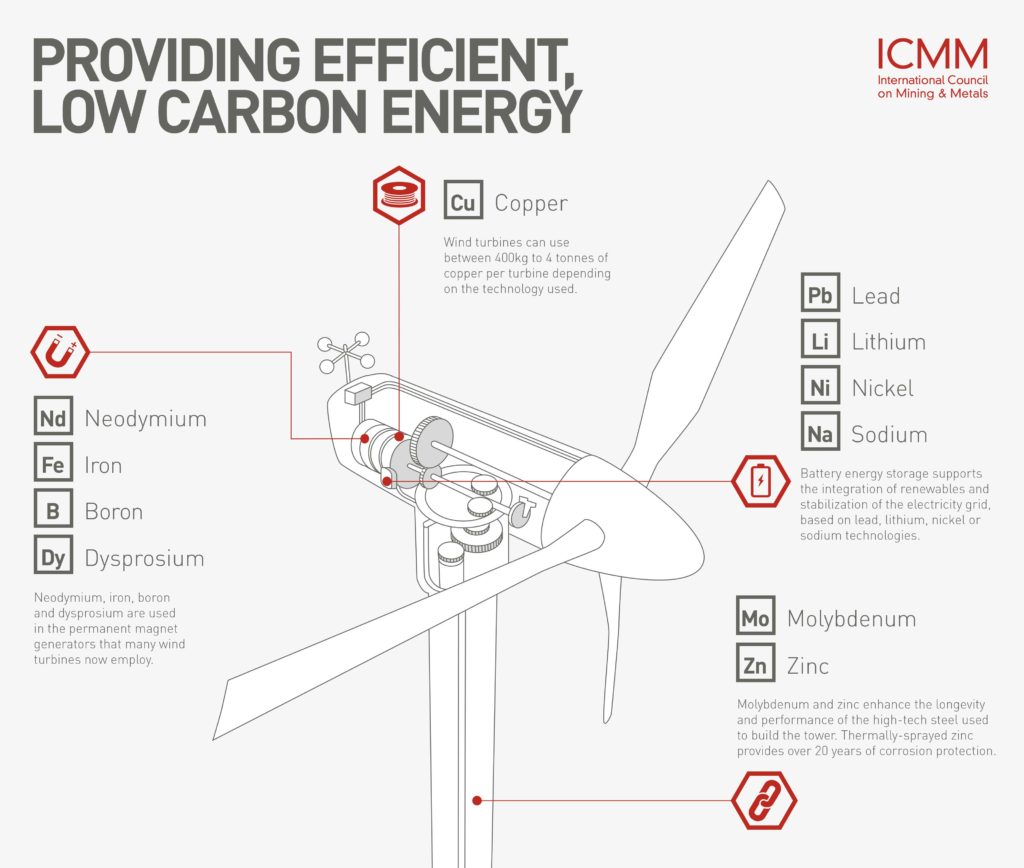
Greenflation is a term used to describe the rising commodity prices associated with going green. This is due to the increased production of renewable energy technologies, which has caused a higher demand for materials.
Example of Greenflation
A commonly discussed example of greenflation is the rising cost of the metals needed for green projects and renewable technologies – lithium for batteries or copper and zinc for solar panels. Implementing more carbon-neutral regulations and increasing environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices may contribute to these rising costs.
Now, the question is: Is the current rising cost of producing renewable energy technologies linked with the global rise in energy prices? In decades, gas, coal and electricity prices have risen to their highest levels.
A combination of factors have caused these increases, but according to IEA, it is inaccurate and misleading to blame them on the clean energy transition.
Global Surge of Energy Prices and the Energy Transition
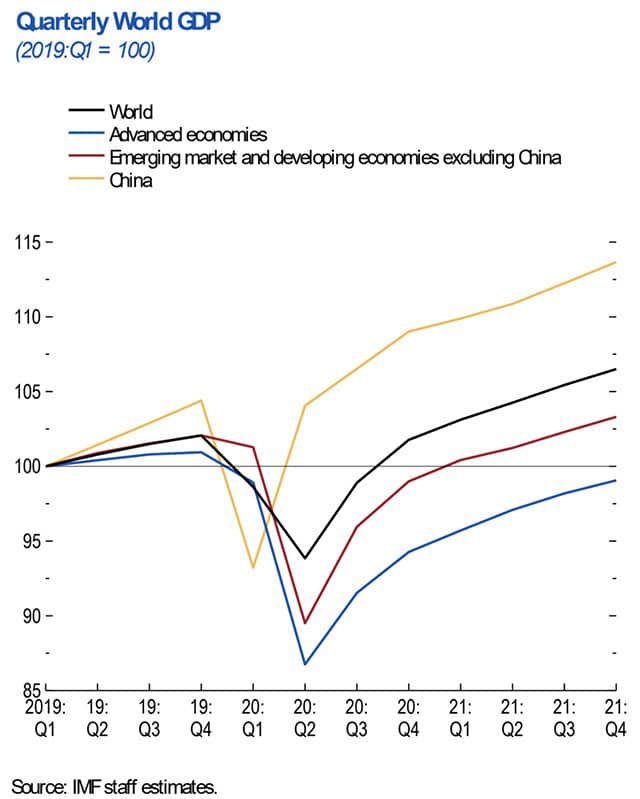
After the historic plunge in global energy consumption in the early months of the pandemic, it has since rebounded strongly. This is mainly due to a rapid global economic recovery and backlogged supply chains. In 2021, the global economy was on track for the fastest post-recession growth in 80 years.
Rising Prices of Fossil Fuels
Natural gas prices have seen the largest increase in the European and Asian markets. US month-ahead natural gas prices more than tripled by the end of 2021 and have reached their highest level since 2008. Also, international coal prices are around five times higher than a year ago. Furthermore, coal power plants in China and India were low in stock before the winter season in 2021.
The dramatic increase in natural gas prices has prompted many countries to use coal as an alternative. The increased use of coal is causing an increase in carbon dioxide emissions from electricity generation globally, which is not helping in dealing with climate change.
The higher gas and coal prices, combined with rising European carbon prices, have resulted in higher electricity prices globally, directly affecting household energy bills and the cost of living.
Some people see the energy transition as the culprit for this increase, but the volatility of the gas market is the leading cause for the hikes in electricity prices.
Greenflation: Risk to Renewable Energy and Global Renewable Energy Market?
While power prices in Europe were steadily increasing, wind and solar were doing a lot of the work, contributing to peak loads from July to September of 2021. The share of fossil fuel output was the lowest since 2016.
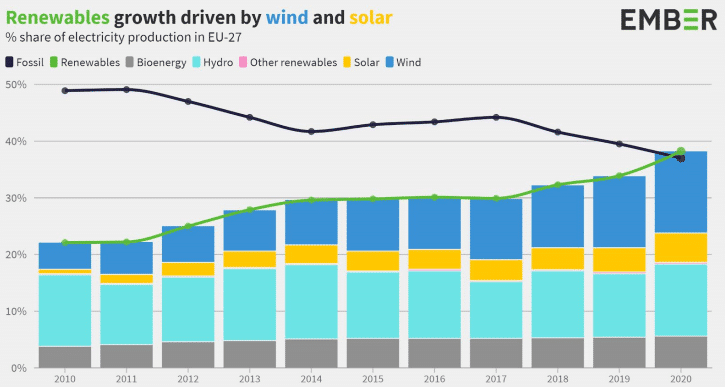
According to the executive director of IEA, blaming greenflation on renewables is baseless. Instead, the energy transition can make markets more stable. Furthermore, if we fail to address the current imbalance in energy investments, the world will continue to face market turbulence and rising energy prices. If the world begins to invest in renewable energy projects and clean energy quickly, we will be on track towards limiting global warming to 1.5 degrees Celsius while also reducing energy market volatility. More solar panels and more wind power plants are needed.
More substantial investments in low-carbon energy will push the world out of the current uncertain energy market. However, this needs to happen quickly. Energy efficiency is a powerful tool for governments, businesses, and consumers to reduce their exposure to market volatility and will enhance resilience.
The Impact of Rising Energy Prices on Asia
Rising gas prices and coal shortages are driving up energy prices in Asia as the region recovers from the pandemic.
The largest economies, like China and India, have many more tools than smaller markets to facilitate this recovery. Smaller and less developed countries are at risk of falling further into poverty.
Without improving energy security, Asia will likely struggle to increase the standard of living and reach universal electrification rates. Countries need to reduce their dependence on fossil fuels to create long-term, successful economic growth.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more