Is LNG the Fuel of the Future?
Source: Fin Shots
17 March 2022 – by Eric Koons Comments (0)
LNG Fuel is fast becoming the go-to form of energy for countries moving away from coal and petroleum. Pundits label Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) as a “transition fuel” as countries shift towards a low-carbon future using renewable energy.
Is LNG a Fuel?
LNG is a fuel, like coal, petroleum, and diesel fuel. Generally speaking, LNG is a safe, versatile fuel source. Burning LNG in its liquid form is possible, as well as reverting it to its gaseous state for other uses. In both cases, LNG has a high energy capacity with its uses spreading throughout society.
Is LNG a Fossil Fuel?
LNG is a fossil fuel, but this high-capacity energy source produces less carbon dioxide and greenhouse gas emissions than other fossil fuels. It can help meet growing power demands in developed and developing countries before a complete shift to clean energy.
China is already one of the world’s leading LNG consumers, and the rest of Asia will follow suit in the coming decades. We expect several projects to come online by 2027 to fill rising energy demands. These projects should improve access and ease natural gas transportation throughout several regions. Global LNG trade and global LNG imports are also rising. As a result, natural gas production has increased along with prices. New LNG export facilities and export terminals are being built to facilitate this growth.
What Type of Fuel Is LNG?
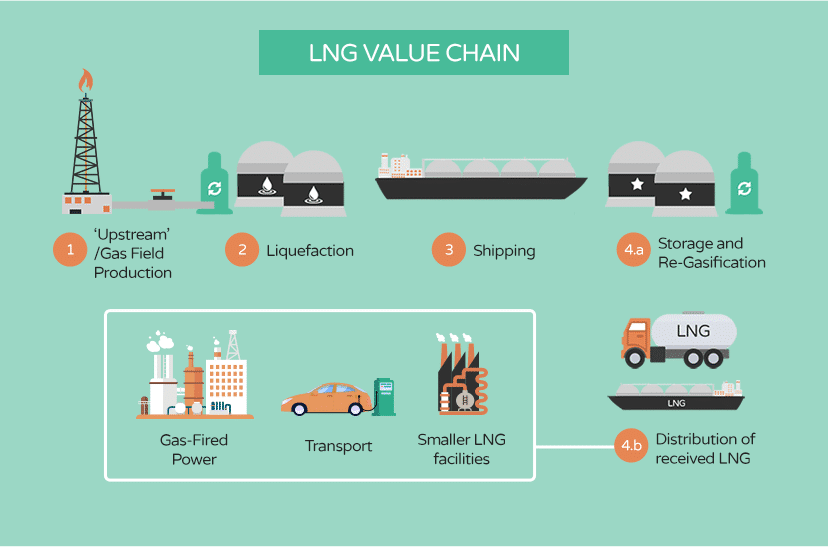
When natural gas is liquefied, LNG results. This happens by cooling natural gas to −162°C (−260°F), where it transforms into a liquid and occupies far less space than as a gas, 1/600th the volume, to be exact. This natural gas liquefaction makes transporting natural gas far more manageable and safer.
While LNG can power vehicles, replacing fuels with higher carbon dioxide emissions, it is often more useful as gas for power plants and electrical grids or heating.
What Is LNG Fuel Used For?
LNG has several uses. Primarily, however, transporting natural gas is its main draw card. After transportation, LNG is often returned to its gaseous state. Shortly after LNG uses range from residential, commercial, and industrial settings for heating, cooking, and generating electricity. Furthermore, and unknown to many, besides using as a transportation fuel, LNG plays a major role in the electric grids in many countries. For example, in 2009, the United States saw natural gas account for over 75% of the commercial and residential sector’s energy needs, 18% of the country’s electricity, and 3% of all vehicles.
How to Transport Natural Gas – Liquefying Natural Gas
When natural gas pipelines are not feasible to transport natural gas, liquefying natural gas is used to do that. This liquefaction process helps transport it to places where the natural gas pipeline can’t reach.
Is LNG Better Than Diesel?
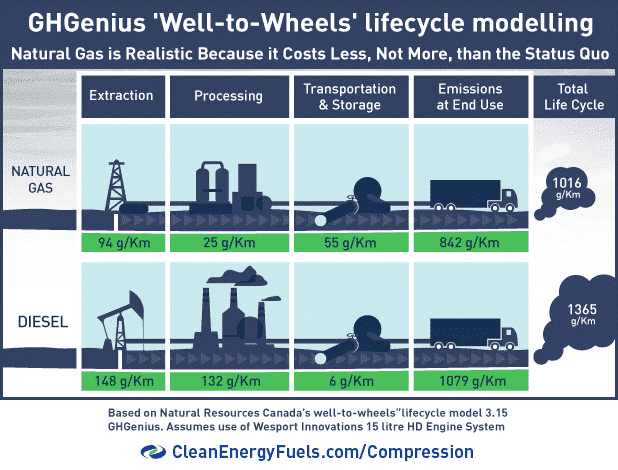
Liquefied Natural Gas is an upgrade over diesel and other fossil fuels. It has a lower maintenance cost, is safe to use and transport, and pollutes up to 90% less than diesel. In terms of cost, diesel can be highly volatile, while LNG is, relatively speaking, more stable yet not immune to price fluctuations. In 2021, for example, LNG experienced unprecedented price swings from lows to highs.
Importantly, natural gas is odourless, colourless, non-toxic, and non-corrosive. In contrast, diesel is highly polluting and has a higher ignition risk. While still a fossil fuel, LNG’s properties make it the cleanest and most efficient fuel out of a dirty bunch.
The Future of the Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) as a Fuel
Global demand for LNG is skyrocketing as the world transitions towards a low-carbon economic system with growing energy demand. LNG fuel is more cost-efficient, produces less carbon dioxide and has more day-to-day applications than many other fossil fuels.
The construction of significant LNG hubs in Asia and other major consuming regions will help ensure there’s enough supply while keeping operating costs and overhead low. As countries move away from fossil fuels like coal, LNG and natural gas will play minor roles in transitioning economies powered by renewable energy.
Go further with LNG
This article is part of our Ultimate Liquefied Natural Gas Guide.
We will discuss more related topics in the following articles, such as what is LNG used for?

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more