Lessons from COP28: South Korea’s Energy Transition Pledges Will Reduce the Need for LNG Investments
Photo: Shutterstock / Stock for you
19 December 2023 – by Michelle (Chaewon) Kim
At the recently concluded 2023 UN Climate Change Conference (COP28) in Dubai, South Korea backed the pledges to triple the global renewable energy capacity by 2030, as well as the nuclear energy capacity by 2050.
South Korea’s ambitious energy transition goals are likely to reduce its liquefied natural gas (LNG) intake, exacerbating the underutilisation of existing and proposed LNG import terminals. A recent report by the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) found that the country is overinvesting in LNG infrastructure despite having among the lowest utilisation rates in the world for regasification terminals.
Despite investing ₩11.3 trillion (US$8.7 billion) in LNG infrastructure for energy security amid geopolitical tensions and domestic market competition, an excessive build-out without aligning with net-zero targets risks binding the economy to costly and unreliable fossil fuel markets.
This could impede South Korea’s swift transition to more affordable and domestically sourced renewable energy.
Lessons from COP28
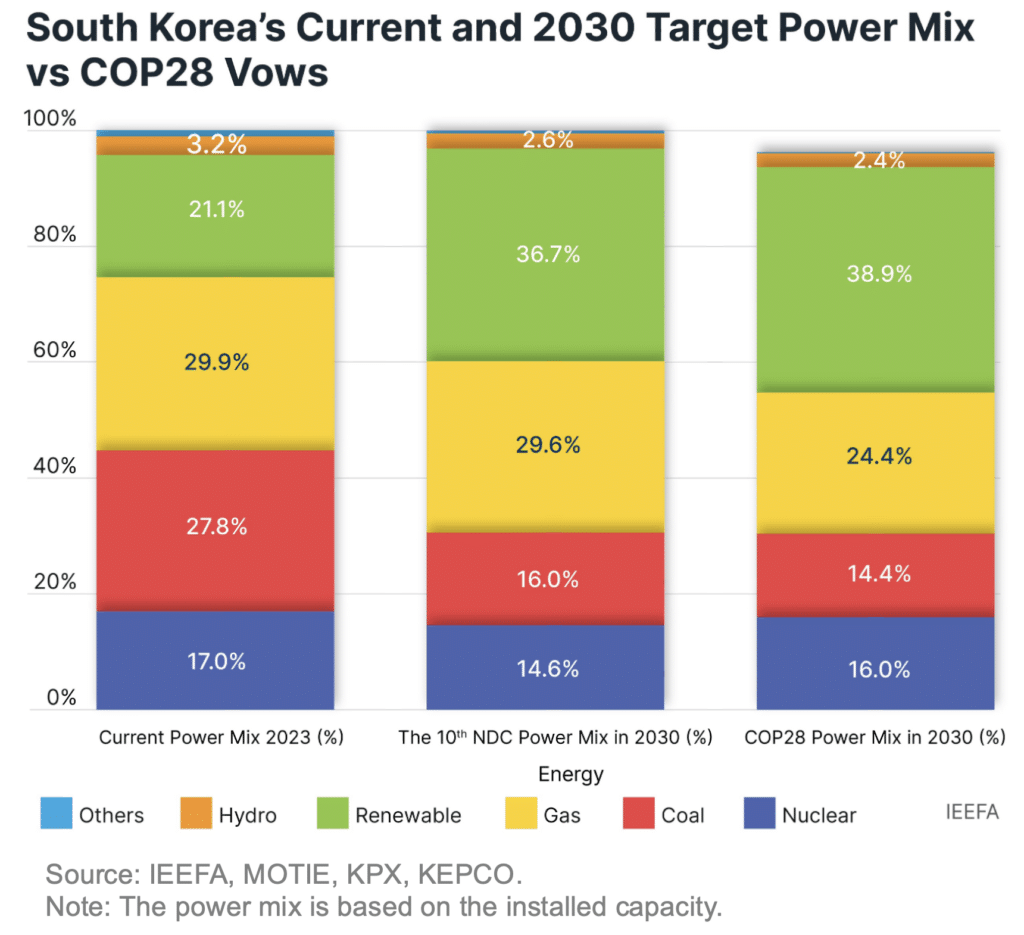
According to IEEFA’s calculation, South Korea’s power mix by installed capacity reflecting the COP28 pledges could reduce the country’s share of LNG to 24.4% by 2030, which is lower than the government’s Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) target of 29.6% by 2030.
By contrast, the share of nuclear and renewables could sharply increase to 16% and 38.9%, respectively.
Burgeoning Overinvestment and Overcapacity
The planned construction of 11 LNG import terminals in South Korea, involving both public and private sectors, poses a high risk of overinvestment and overcapacity. This risk is driven by a growing misalignment between the expanding LNG infrastructure and the projected demand, as per the country’s net-zero goal.
New LNG terminals, if built, would increase the country’s total regasification capacity to 190 million tonnes per annum (MTPA) by 2036. By contrast, LNG demand is expected to decline to 37.66 MTPA, down 20% from 2022. The South Korean government’s climate targets project that the share of LNG in the power mix will fall to 9.3% in 2036, from 27.5% in 2022. Based on IEEFA’s calculations, the regasification facility utilisation would decrease drastically from 29.48% in 2023 to 19.78% in 2036.
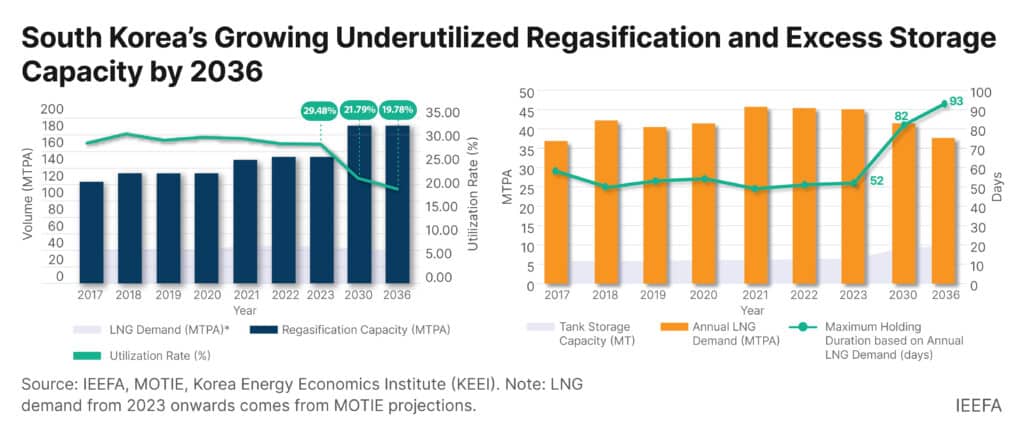
Along with import terminals, developers are also building out LNG storage capacity. Proposed LNG storage projects are estimated to fulfill 25.6% of the annual LNG demand in 2036, a nearly double increase from the 2023 level of 14.1%. In practical terms, the planned storage capacity would accommodate approximately 93 days’ worth of LNG demand in 2036, representing a 79% increase from the current 52 days. This surpasses the government’s mandated target of nine days of peak winter demand.
The notable disparity between the infrastructure expansion and the anticipated demand, based on the country’s latest NDC to the Paris Agreement, indicates a lack of alignment with national net-zero goals for new LNG projects. Additionally, in line with the “COP28 tripling pledges,” countries are expected to enhance their NDCs every five years as mandated. South Korea will therefore submit a more ambitious target in 2025 that could further reduce the need for new LNG infrastructure.
Binding to Uncertain and Volatile Fossil Fuel
LNG markets have experienced extreme volatility amid geopolitical uncertainties, which has undermined the fuel’s affordability and reliability. Following the Russian invasion of Ukraine, LNG spot prices in Asia spiked to record levels of over US$80 per million British thermal units (MMBtu) in March 2022. Prices have since fallen to US$16/MMBtu in December 2023 but remain more than 20% over the previous five-year average.
High fuel costs have driven up the price of power generation in the country. In November 2022, the cost of LNG-fired power generation reached a historic ₩270.38 (US$0.21) per kilowatt-hour which is more than double the prices one year earlier.
Volatile LNG prices, combined with South Korea’s declining natural gas demand, will likely erode the economic case for new LNG infrastructure, raising inefficiency and stranded asset risks. This is especially true as the country deploys larger amounts of relatively low-cost renewable energy. While LNG fuel costs for power generation have nearly doubled from a year ago in 2022, the cost of power generation from solar and wind, for example, was between ₩128-166/kWh last year — edged up only 1-8% on-year, significantly less volatile than imported LNG.
Moreover, the belief in repurposing existing infrastructure for blue hydrogen production and greenhouse gas capture is considered premature and controversial. The International Energy Agency notes that “hydrogen production is more of a climate problem than a solution.” An IEEFA review of carbon capture facilities found that a majority of the world’s flagship projects either failed or underperformed capture targets.
Ultimately, the state-run firms’ excessive LNG terminal investment is poised to put a heavier financial burden on taxpayers, while private companies’ overinvestment may destabilise investors and result in higher utility bills. Instead, public-private collaboration should optimise existing terminals and avoid promoting uncertain ventures that prolong LNG use.
Global renewable energy targets and more ambitious climate targets should serve as a wake-up call for the South Korean government to align the country’s LNG infrastructure and demand with net-zero targets.
About IEEFA
IEEFA is an independent think tank that examines issues related to energy markets, trends and policies.
Disclaimer: The views and opinions expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of Energy Tracker Asia.




