5 Biggest Advantages and Disadvantages of Natural Gas
09 June 2024 – by Eric Koons Comments (0)
As the world has begun to move on from fossil fuels, many are viewing natural gas as a transition fuel towards a clean energy future. So, what are the advantages and disadvantages of natural gas? A high-capacity energy provider, natural gas is becoming the go-to power source for countries with growing economies and rising electricity demands.
It can be used in the form of liquefied natural gas (LNG), liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), or compressed natural gas (CNG). There are many advantages of using natural gas over coal; some are mentioned below.
As such, global natural gas demand is increasing, and Asia will become one of the largest natural gas consumers in the coming decades. This is evidenced by major liquefied natural gas (LNG) projects that are being undertaken in Singapore and India. Keeping that in mind, here are various pros and cons of natural gas.
Advantages of Natural Gas – Pros
Here are some of the top benefits of natural gas:
1. Natural Gas is Abundant
One of the good things about natural gas is that it is an abundant natural resource. The International Energy Agency (IEA) estimates there are enough recoverable natural gas resources to last around 230 years. Natural gas deposits are found around the world, making it easier for extraction and supply, potentially keeping prices low as long as the adequate infrastructure is present.
2. Low Carbon Dioxide and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Though burning natural gas releases greenhouse gases, it still expels the least amount of carbon emissions of all the fossil fuels, so natural gas produces less pollution. This, in tandem with its high energy output, is the reason it is a natural bridging fuel. Consequently, this makes it a logical successor to coal and petroleum. Its low carbon emissions have made it an appealing power source for developed and developing economies.
3. Rapid and Efficient Transport
When it is cooled to −161.5 °C, natural gas becomes a liquid (LNG), filling only 1/600th of its original volume. This makes natural gas easier to store and transport long distances. When pipelines are available, natural gas is relatively easy to transport in its gaseous form. Natural gas supply chains are well established, with supply routes by sea and land serving several major hubs. New hubs and transport infrastructure will come online during the decade, further improving the rapidity and efficiency of the world’s gas supply.
4. Versatile Energy Source
Another advantage of natural gas is its versatility. As a gas or as LNG, it can power electrical grids, heating systems, home cooking appliances, and some vehicles. It is natural gas’ versatility that increases its popularity and demand. This is especially true for developing countries, with natural gas playing a prominent role in emerging economies globally.
5. Natural Gas is less Expensive than other Fossil Fuels
Natural gas production is much less expensive than other fossil fuels such as oil or coal. It is used for power generation because it costs less.
Disadvantages of Natural Gas – Cons
Here are some of the disadvantages or limitations of natural gas:
1. Natural Gas is a Fossil Fuel
Gas’ carbon emissions are lower than other fossil fuels. However, it still is a fossil fuel. Natural gas is not renewable, except in very specific circumstances. Either way, it produces more carbon dioxide than green energy. This is why it is a bridging fuel. It fills the gap between the decommissioning of larger fossil fuel plants and the growth of renewable energy on a large scale.
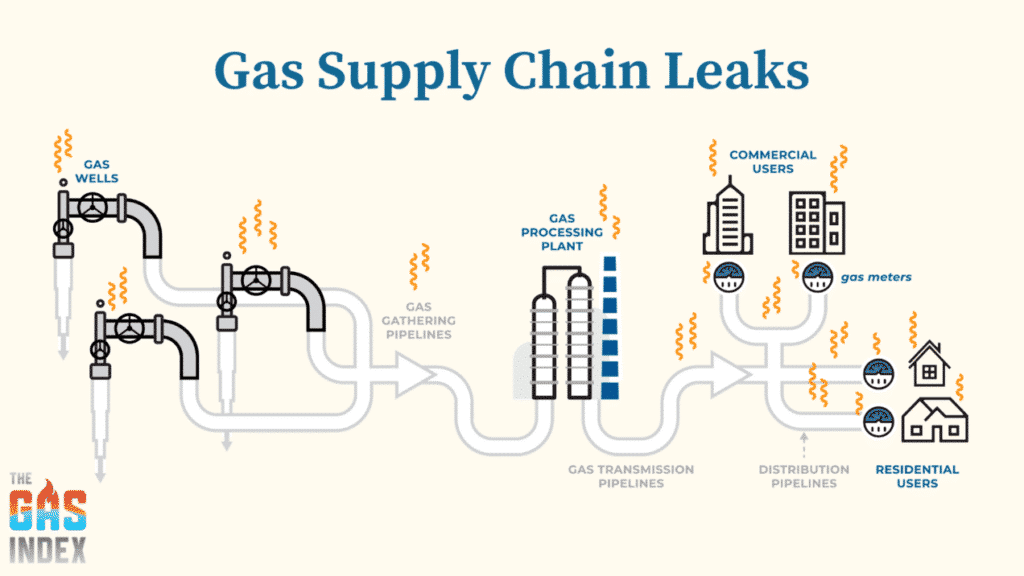
2. Methane Leaks
Natural gas is easy to transport and comes from global locations. However, these activities release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, at every level of the supply chain. The global warming potential of methane is 28 to 34 times higher than carbon dioxide. Methane leaks are hard to avoid, making natural gas a dirtier energy source than initially thought. This, combined with the fact that natural gas is a greenhouse gas, further emphasises its status as a fossil fuel.
3. Price Volatility
Russia largely controls the natural gas market in Europe and, to some extent, Asia. Issues with transport and political tensions have led to volatile natural gas prices in both regions. To keep prices stable and supply constant, infrastructure is under development in Europe and Asia that will come online after 2023. Looking at the United States, where natural gas supply chains are entirely domestic, prices are lower.
4. Sourcing Natural Gas
There are several ways of extracting natural gas, but fracking is one of the most common. Fracking involves pumping water into an underground gas deposit to bring it closer to the surface. It has been linked to several major health issues, environmental damage, and large methane leaks. In the United States, fracking makes up 67% of gas sourcing. While new projects emphasise a shift towards a more sustainable extraction process, fracking remains a cheap and popular sourcing option.
5. Natural Gas is Dangerous
Natural gas is a highly flammable substance and combustible material. It can cause more damage if natural gas leaks.
Do the Advantages Outweigh the Disadvantages of Natural Gas?
Natural gas has several significant advantages and disadvantages that can cancel each other out in some cases. Its high-energy capacity, ease of transportation and low carbon dioxide emissions make it a reliable candidate as a transition fuel. However, methane leaks from supply chains, sourcing issues, and its status as a fossil fuel raise questions.
On the other side, natural gas is versatile, making it ideal for expanding economies. Price volatility will likely decline once infrastructure projects are completed later in the decade. The debate surrounding natural gas’ role as a bridging fuel is sure to continue, but one thing is for certain: natural gas will play a major role in the global transition towards a low-carbon future.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more






