The Advantages and Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy
Source: CNBC
12 December 2024 – by Eric Koons
There are many advantages and disadvantages of nuclear energy, but the disadvantages of nuclear energy have hindered its growth over the last two decades as renewable energy has increased exponentially. Despite producing around 9% of global electricity in 2023, its total electricity production is about equivalent to what it was in 2000.
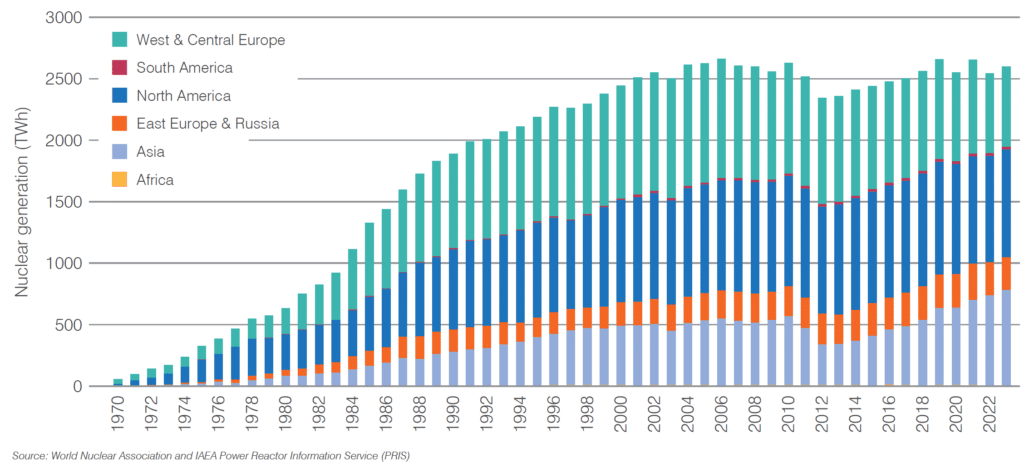
Historically, nuclear energy surged after the 1970s oil crisis, promising a stable and efficient power source. However, high-profile accidents like in Three Mile Island in 1979, Chernobyl in 1986 and Fukushima in 2011 triggered global reevaluation. Countries like Germany have since initiated plans to phase out nuclear power, shifting attention to renewable alternatives.
What Is Nuclear Energy?
Nuclear energy is produced through nuclear fission – primarily with uranium – by splitting the nucleus of an atom into smaller parts. In nuclear reactors, uranium-235 atoms are bombarded with neutrons, which cause them to split, releasing heat energy and additional neutrons. These neutrons continue to trigger fission in other uranium atoms, creating a sustained chain reaction.
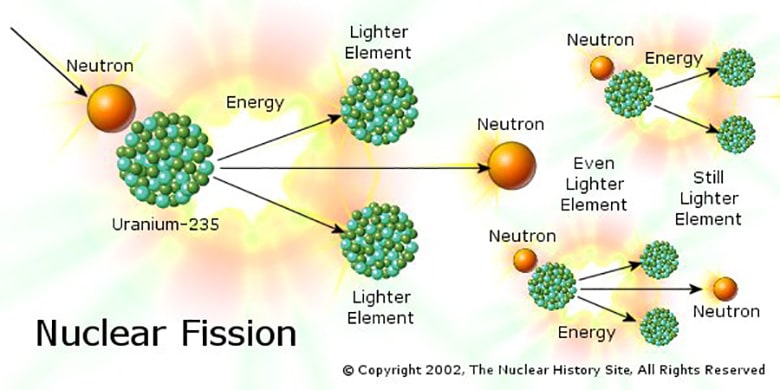
The heat generated is used to produce steam that drives turbines to generate electricity. This process yields a massive energy output from a small amount of fuel. While this can seem like a great way to continually and reliably generate energy, nuclear energy does have several disadvantages. Yet even with those disadvantages, nations in Asia like China and India have invested heavily in nuclear power to meet their growing energy demands.
Below are some of the pros and cons of nuclear energy:
Advantages of Nuclear Energy – Pros
1. High Energy Density
Nuclear fuel has an exceptionally high energy density. One kg of uranium can produce 20,000 times as much energy as the same amount of coal. This efficiency reduces the frequency and volume of fuel sourcing compared to fossil fuels.
2. Low Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Nuclear power plants emit minimal greenhouse gases while operating, which is good for climate change. This typically ranges from 15-50 grams of CO2 (gCO2) per KWh, compared to 450 gCO2 for natural gas and 1,050 gCO2 for coal. The world’s existing nuclear reactor fleet helps avoid 1.5 gigatonnes of emissions annually.
With that said, nuclear energy is not renewable and relies on finite resources. The ongoing mining, refining and production of reactor fuels are energy- and emissions-intensive if not powered by renewables.
3. Reliability
Nuclear power plants operate with the highest capacity factor of any energy source and can run continuously. For example, during 2021, nuclear power plants in the United States produced energy for 92% of the year. This was twice as reliable as coal and natural gas. This reliability provides a stable baseload energy supply to the nuclear power industry for meeting consistent electricity demands without interruption.
4. Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels
As with all alternative, low-carbon fuel sources, nuclear technologies can reduce reliance on fossil fuels. For many countries, this provides domestic energy production rather than relying on fossil fuel imports, improving energy security and diversifying the energy mix.
Disadvantages of Nuclear Energy – Cons
Despite these advantages of nuclear energy, several significant disadvantages make nuclear energy a contentious choice. Ultimately, these disadvantages of nuclear energy make renewable energy sources the superior option for most countries as they undergo long and short-term energy transitions away from fossil fuels.
1. Nuclear Waste Management
Nuclear reactors produce radioactive waste as a byproduct that remains hazardous for thousands of years. Safe, long-term disposal solutions, such as deep geological repositories, are complex and expensive, posing environmental and logistical challenges. This means that nearly all of the world’s existing nuclear waste is stored in temporary facilities. As more radioactive waste is produced, new storage facilities must be constructed.
2. High Capital Costs
Constructing nuclear power plants demands substantial investment. Estimates show that costs range from USD 5,500-8,100 per kW of capacity at a nuclear plant. So, for a 1,100 MW plant, this is between USD 6 billion and USD 9 billion.
Compared to the cost of utility-scale solar and wind, the cost of nuclear is prohibitive. Additionally, if investment flows into nuclear energy, it will likely take away from investment flowing into renewables. Lower-cost renewables will expedite low-carbon energy production and speed up the global energy transition.
3. Risk of Nuclear Accidents – Explosions of Nuclear Power Plants
Historical incidents like Chernobyl and Fukushima highlight the catastrophic potential of nuclear accidents. The Fukushima disaster in Japan in 2011 led to over 150,000 people being evacuated and an estimated economic loss of USD 200 billion. As of 2020, 41,000 people were still living as evacuees, unable to return to their homes due to high levels of radioactivity. As a result, the country immediately shut down its 54 nuclear reactors and the energy supply gap was filled by fossil fuels. This set back the country’s energy transition, which is still slow to progress today.
4. Limited Uranium Resources
Uranium, the primary fuel for nuclear reactors, is a finite resource. According to the World Nuclear Association, current identified resources will last for about 90 years at present consumption rates. However, if nuclear energy capacity grows, resources will be depleted faster.
Ultimately, this means nuclear energy is not a complete solution to the world’s energy needs. Alternatively, renewable resources are not depleted and will forever remain viable. Furthermore, dependence on uranium can lead to supply vulnerabilities and geopolitical tensions over resource control.
Choosing Renewable Energy: The Path Toward Sustainable and Safe Energy
While nuclear energy offers several advantages in the near- and medium-term, the disadvantages of nuclear power pose considerable challenges and reduce its long-term viability. Renewable alternatives like solar power, wind and hydroelectric power present safer and more sustainable options.
These technologies have seen significant cost reductions, with solar becoming Asia’s cheapest source of new power during 2023. Investing in these alternatives can meet the world’s growing energy needs while minimising environmental risks and fostering energy independence.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more








