The Pros and Cons of Hydrogen Energy
werbung / Shutterstock.com
09 February 2023 – by Eric Koons Comments (0)
Pros and Cons of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
There are many pros and cons of hydrogen energy. While hydrogen energy has the potential to be clean, it is not a primary energy source. Instead, it is a way to store and transfer energy already generated. As a result, the emissions that come from hydrogen are heavily reliant on the input energy. So, there are many advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen energy.
This poses several drawbacks and challenges to hydrogen energy production and use. Regardless, hydrogen has a vital role in the world’s energy transition. Understanding and addressing these pros and cons of hydrogen energy is crucial to the effective implementation of hydrogen power as the world moves towards a net-zero future.
How Is Hydrogen Fuel Made?
Hydrogen fuel can be produced through a variety of methods, but the two most common methods of producing hydrogen energy are water electrolysis and thermochemical processes.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydrogen Energy
The Pros of Hydrogen Energy – Advantages
1. Clean Energy
One of the main advantages of hydrogen energy is that it can be a clean energy source. Unlike fossil fuels, which emit pollutants and greenhouse gases when burned, hydrogen only produces water vapour when used as a fuel. If we use renewable energy to produce hydrogen, there are no direct emissions. Hydrogen made with renewable energy sources is known as green hydrogen. Hydrogen made from fossil fuels, such as natural gas, is called grey hydrogen.
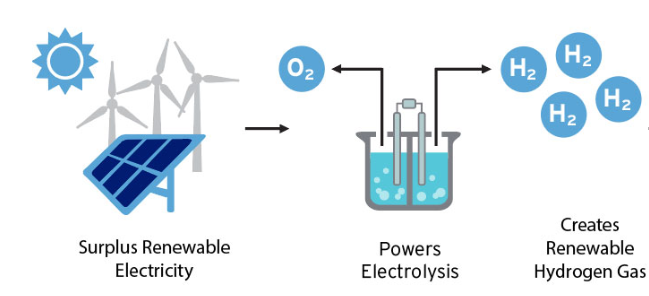
2. Storing Renewable Energy
Hydrogen provides a viable way to store renewable energy for an extended period. Intermittency and storage are both significant issues facing renewables. Currently, batteries are less energy efficient and less cost-effective than the global energy transition needs.
Utilising hydrogen as a storage medium will promote and facilitate renewable energy use and help fighting global warming. Through these pathways, sustainable hydrogen energy or green hydrogen can significantly reduce carbon dioxide emissions and help mitigate climate change. According to the International Energy Agency, hydrogen has the potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 60 Gt between 2021 and 2050.
“Green hydrogen could be a critical enabler of the global transition to sustainable energy and net zero emissions economies.”
Abhinav Chugh (World Economic Forum) and Emanuele Taibi (International Renewable Energy Agency)
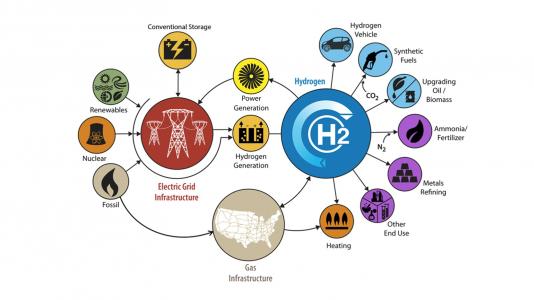
3. Hydrogen Is Versatile
One of the pros of hydrogen energy is that it is very versatile. It can generate electricity, heat buildings, power vehicles and even produce industrial chemicals. This makes hydrogen energy a potential solution for a wide range of applications such as hydrogen powered vehicles. This variability is highly beneficial for hard-to-decarbonise industries that lack many viable renewable energy alternatives.
One of the applications growing in popularity is hydrogen fuel cells. Hydrogen fuel cell technology is a potential game changer for the transportation industry, particularly for vehicles that are unsuitable for plug-in battery solutions. Both planes and heavy-duty trucks fit this category because they depend on weight. Hydrogen is a light alternative to heavy batteries.
4. Renewable Energy
Hydrogen energy is also a renewable energy source when produced using electrolysis. Electrolysis produces hydrogen by splitting water into oxygen and hydrogen gas. This hydrogen production process can be continuously done as long as there is water and energy. When electrolysis uses renewable energy, the direct carbon footprint is near zero.
Cons of Hydrogen Energy – Disadvantages
1. Production and Storage Costs
However, hydrogen energy has several significant drawbacks. One of the biggest disadvantages of hydrogen energy is the cost of producing and storing hydrogen. Currently, the process of electrolysis is relatively expensive and energy intensive. Additionally, hydrogen is a gas at room temperature and must be stored in high-pressure or cryogenic tanks. The infrastructure to complete this process is cost prohibitive.
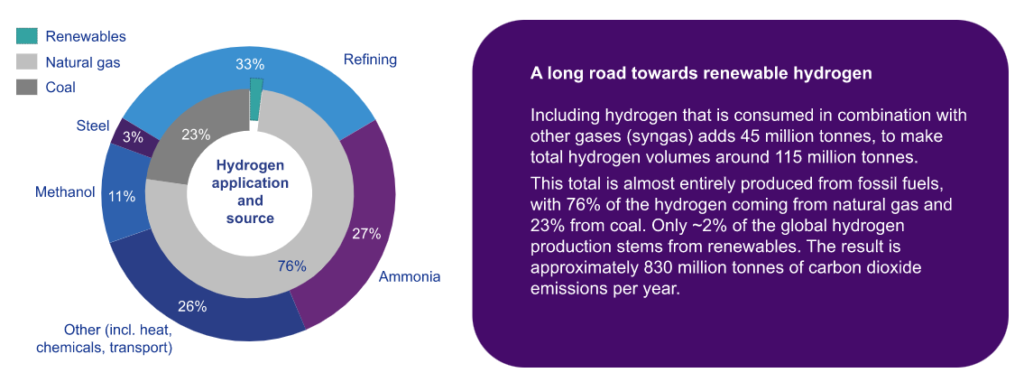
According to the International Energy Association (IEA), the cost of producing hydrogen with low-carbon energy ranges from USD 3.2 to USD 7.7 per kilogram. However, technological advancements will decrease these costs in the coming years. By 2060, the IEA predicts production costs to be closer to USD 1.3 to USD 3.3 per kilogram.
2. Lack of Infrastructure
One of the cons of hydrogen energy is the lack of infrastructure. While hydrogen vehicles and power plants exist, there are not enough to support the widespread use of hydrogen as a fuel source. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, there were only 48 hydrogen fueling stations in the United States by mid-2021.
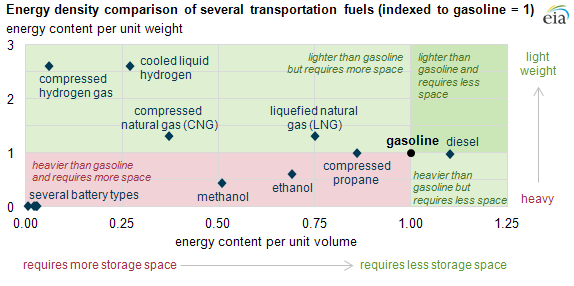
3. Energy Density
Finally, hydrogen has a low volumetric energy density. Uncompressed, the amount of energy in 1 L of hydrogen is about one-fourth of the amount in gasoline. However, when it is compressed into a liquid, the energy density is three times greater than gasoline. As previously discussed, compressing hydrogen is an expensive process, which adds to the financial roadblock of hydrogen adoption.
Is Hydrogen a Viable Energy Source?
In conclusion, hydrogen energy has several pros and cons. While it can be a clean and renewable energy source, the cost of producing and storing hydrogen currently needs to be lowered for widespread adoption.
With a lack of infrastructure and high costs, hydrogen energy is not viable in its current state.
However, there is growing interest in the field, and more financing is going towards mitigating its challenges. For example, the United States just announced USD 52.5 million for hydrogen development, and the European Union is putting USD 5.2 billion towards similar projects.
If governments worldwide follow suit, hydrogen can become a cost-effective and sustainable energy source in the future.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more
