Top 10 Uses of Natural Gas
Photo by Mike Mareen via ShutterStock
04 April 2024 – by Eric Koons Comments (1)
What Is Natural Gas Used for?
From energy generation to cooking and heating fuel and transportation, there are many uses of natural gas within the global context. Its versatility leads to strong support for a growing presence within energy portfolios – especially as a transition fuel between other fossil fuels and renewable energy sources. Natural gas production has increased globally.
The prevalence of natural gas within society is leading to debates about its advantages and disadvantages. Additionally, it creates a discussion on how to use fossil fuels in light of global low emissions goals.
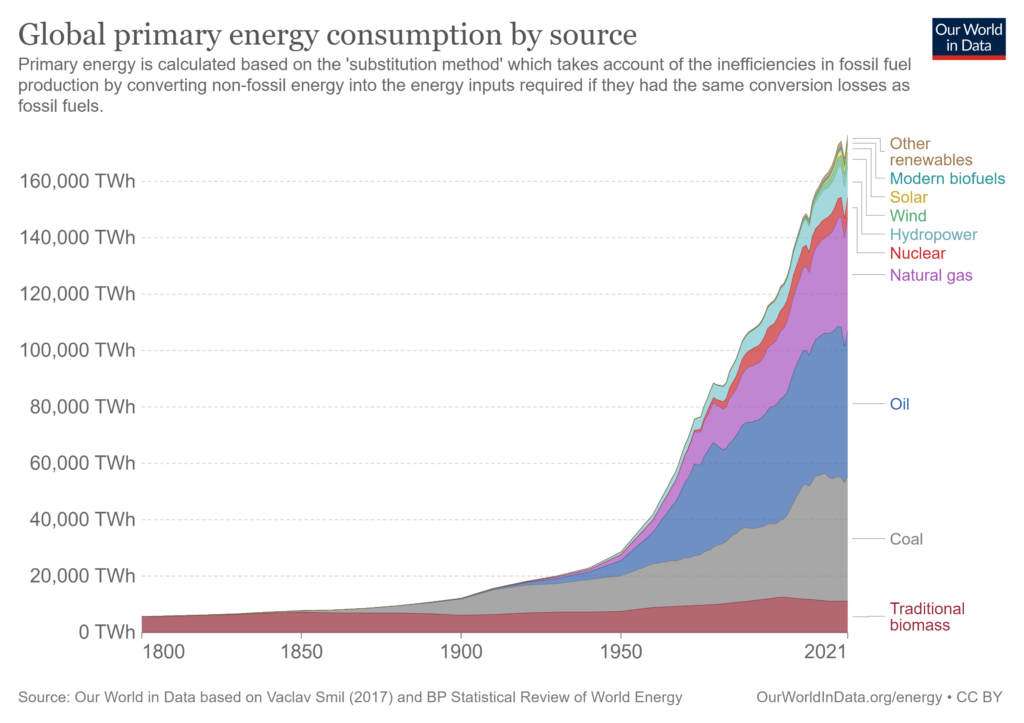
Use of Natural Gas
In 2021, natural gas accounted for roughly 24% of global energy consumption, trailing only oil and coal. Demand is growing as nations seek cheap, high-capacity energy sources, whether it’s compressed natural gas or liquefied natural gas. The International Energy Agency (IEA) noted in a recent report that half of the total natural gas demand comes from the Asia-Pacific region as it looks to power its growing industrial and residential needs.
10 Uses of Natural Gas – Examples
Out of the many uses of natural gas, the ten most common are:
1. To Generate Electricity
Natural gas is a top-three energy source globally. While it is the least polluting of the three fossil fuels, it is almost as energy dense. It still does produce greenhouse gas emissions, which raises questions about its long-term viability.
2. Heating
For many households, natural gas is the default heating source due to its efficiency and ease of use. It is estimated that almost half of homes in the United States are heated using gas.
3. Transportation
An often overlooked aspect of natural gas, it does have a presence within the transportation sector. Although market share is dominated by petroleum (92%), natural gas vehicles make up 3% and electric vehicles make up less than 1% of the market.
4. Production
Natural gas is crucial for producing chemicals, fertilizers and hydrogen. A third of all natural gas consumed in the United States is in manufacturing.
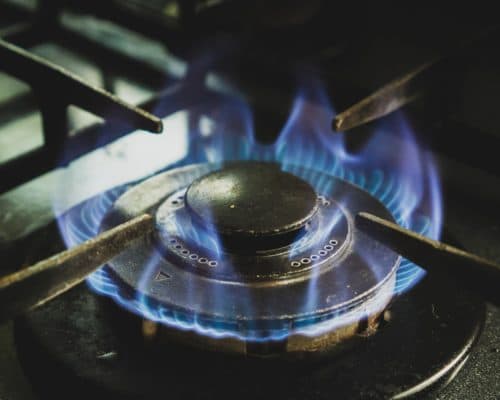
5. Cooking
While several campaigns are underway to reduce the prevalence of natural gas stovetops, it remains one of the world’s most used cooking fuels.
6. Water Heating
Natural gas is the preferred option for many home needs, such as general heating or water heating. This is due to its fast heating times and relatively low cost of operation.
7. Air Conditioning
Gas-powered models exist but are not as popular as other variants.
8. Fire
Controlled fires, whether in a chimney or outdoors using a barbecue, benefit from natural gas. Natural gas is safe, easy to use and controllable, making it a staple in many homes.
9. Commercial
Along with the industrial sector, commercial natural gas use is high. It is used in manufacturing and for general uses associated with operating physical premises.
10. Economic Development
Natural gas fields can be an economic boon for nations and can facilitate economic growth. However, the environmental impact of gas extraction and processing can create their own problems.
Natural Gas Usage for Electricity Generation
While natural gas is a versatile energy source, its primary use is power generation. This demand mainly comes from its high energy density and historically low price. However, recent price volatility and supply issues may impact the market in the future.
Another major consideration is that natural gas produces fewer carbon dioxide emissions than coal and oil, which has led some groups to paint it as a “greener” fossil fuel. Unfortunately, some markets view it as a green energy source.
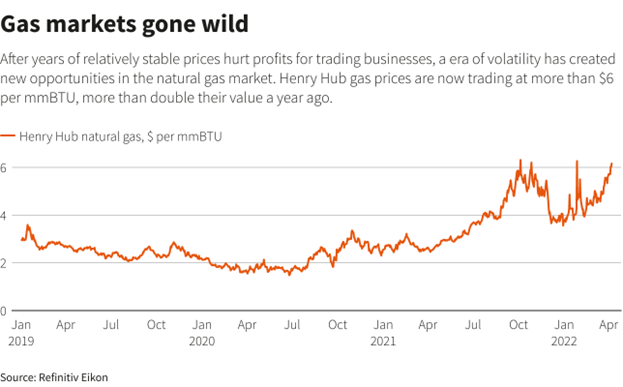
However, natural gas is not renewable and primarily consists of methane. Methane is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential 25 times higher than carbon dioxide. Additionally, natural gas infrastructure can have ongoing leak issues.
Many people see marketing natural gas as a transition fuel as greenwashing. Regardless, the need to meet growing energy demand, especially in Asia, is driving countries to still turn towards natural gas instead of renewables.
Where is Natural Gas Consumption the Highest?
The United States, Russia, China, Iran and Japan are the world’s largest natural gas consumers. The US alone is responsible for 21.7% of global natural gas use.
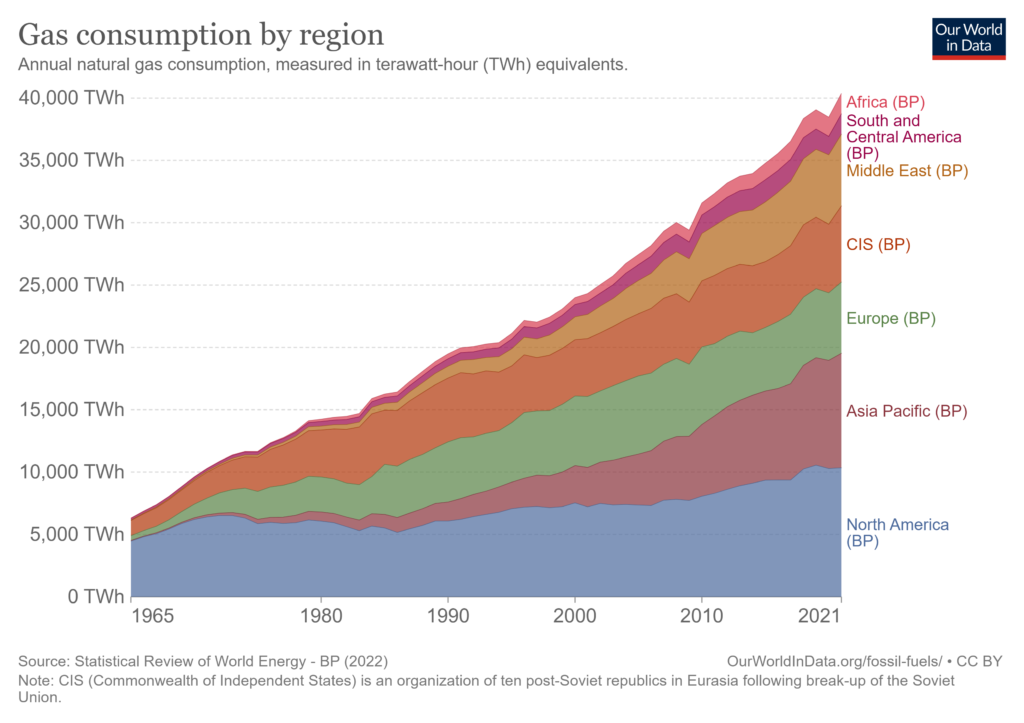
In terms of demand, the war in Ukraine has led to a global surge in demand, especially in Europe, where Russia is historically the EU’s leading supplier. The Asia-Pacific is expected to be the biggest demand driver in the coming years as it continues developing and improving its infrastructure.
A Complicated Future
Touted as a bridging fuel capable of helping the transition to low-carbon economies, the use of natural gas is a topic of fierce debate. Current United Nations climate change chief Simon Stiell has previously described natural gas as “a bridge to nowhere” – a sentiment shared by many on the international stage. But, with continued demand, growth and production, it is not easy to see how natural gas will be dealt with in the future.
With fossil fuels already branded as a stranded asset by major insurers like AIA, we can only hope natural gas does not seem like a long-term alternative and true renewables continue to grow in market share.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more






