Best Renewable Resource Examples in Energy
22 June 2022 – by Eric Koons
What are the best renewable resource examples? This is a question that comes up regularly when its comes to clean energy. Generally speaking, it boils down to the rate a resource is used and replenished. Energy sources defined as renewable resources replenish over a relatively short period of time, naturally. A list of renewable resource examples include wind, the sun, moving water, the earth’s heat and organic waste. Governments across the world are now readily rolling out renewable energy resources to power peoples lives. Ultimately, these renewable energy resources will replace fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas.
Three Examples of the Main Renewable Resources
How Is Wind Energy A Renewable Resource?
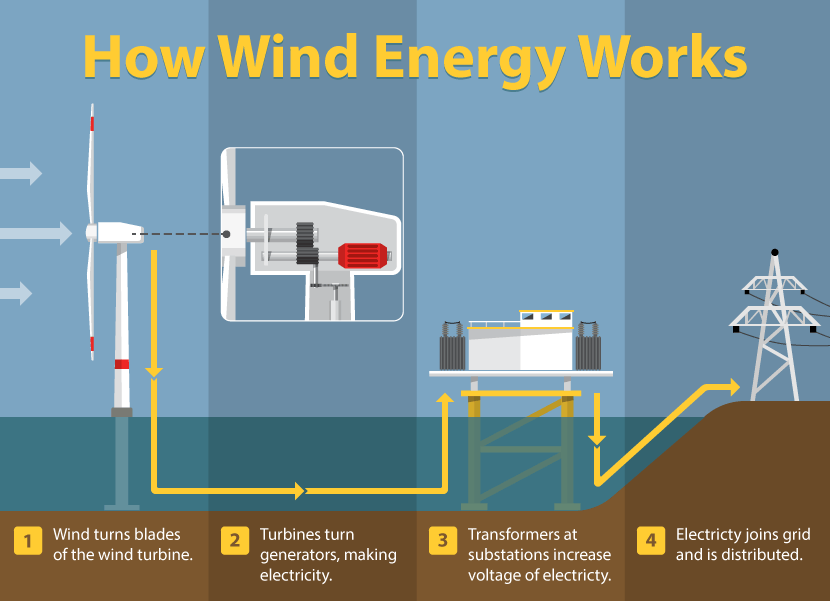
Wind is a renewable resource that is converted into electricity by capturing kinetic energy with wind turbines. They vary in size and can produce power for homes and utility scales. Wind power is a type of renewable resource that is clean, sustainable and available on a global scale. One of the main advantages of wind is from the ability to generate electricity without carbon emissions, opposed to power plants burning fossil fuels.
The capacity factor – total amount of time for power production – for wind ranges from 41 to 44%. Whereas the levelised cost of electricity (LCOE) – the price of electricity for a project’s revenues to equal its costs – ranges from USD $36.93-$120.52 per megawatt-hour.
Renewable Energy Resource From the Sun – Solar
Solar is a common renewable resource. Captured by converting sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) panels or source concentrating mirrors (CSP). Solar power is a renewable energy that can be utilised anywhere during the day and generate power. Like its counterpart wind, solar does not create any carbon emissions when producing electricity. It is one of the cleanest sources of energy available.
Similar solar power processes can produce utility-scale power, water heating, lighting and portable solutions. The capacity factors and LCOE for solar vary, but an average solar PV plant has a capacity factor of 28.5% and LCOE of USD 37.50 per megawatt-hour. Globally, China accounts for the greatest solar energy capacity, followed by the United States, Japan and Germany. Other countries like India and Vietnam are investing heavily in solar power, adding to Asia’s goal of becoming a global leader in solar energy.
Generating Renewable Energy Through Moving Water – Hydropower
Another renewable resource example is moving water. The movement converts into electricity by capturing the kinetic energy – like wind – with rotating water turbines. Hydropower is a utility-scale power source, which can also utilise batteries for storage. Additionally, run-of-the-river systems and tidal flow energy systems are smaller-scale hydropower systems.
Asia accounts for roughly half of the globes hydropower facilities, with China first and followed by Japan, Vietnam and India, respectively. Hydropower, is another clean renewable resource and does not produce carbon emissions while creating electricity. For example, the Xiluodu Hydroelectric Power Plant on Jinsha Jiang River in China offsets about 150 million tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions annually.
Compared to solar energy, hydropower has a significantly higher capacity factor and LCOE. They come in at 55% and USD 55.26 per megawatt-hour.
Another List of Renewable Resources
Renewable Energy From the Earth’s Heat – Geothermal
While not as popular as the first three renewable resource examples, heat beneath the Earth is a powerful energy source. Capturing the heat and pressure, and producing electricity is known as geothermal power.Water and/or steam transfers the energy to the Earth’s surface and converted into electricity.
Geothermal has proven useful in providing clean carbon free electricity to households and at utility scale. This type of renewable energy still has a long way to go before it can meet the demands of rapidly-developing Asian countries. However, it is an example of a high potential renewable power source growing in popularity. In Asia, it was first trialed in 2006 at Kamphamgpet, Thailand.
Working in it’s favour, Geothermal power’s capacity factor and LCOE averages at around 90% and USD 34.49 per megawatt-hour.

Transforming Waste to Clean Energy – Biomass
With huge potential, biomass is another example of a renewable resource. Generally, biomass umbrella term for waste sourced from wood, agricultural residues and other organic waste. Used in certain ways, like burning or through chemical reactions, biomass can produce useable energy. In some cases, biomass can create liquid fuels used to power vehicles, known as biofuels.
The capacity factors and LCOE for biomass are the second highest out of all the renewable energy examples mentioned. They stand at 83% and USD 89.21 per megawatt-hour.
Biomass is a renewable resource competitive with fossil fuels. However, it largely depends on a country’s natural resource access. In the future, biomass looks set to play an integral part in the clean energy transition, especially in Asia.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more



