Asia’s Risk From Heat – An Inconsistent Renewable and Sustainable Energy Transition
A young boy dives into a polluted river to escape the heat in Central Visayas in the Philippines. Image: AdamCohn
27 August 2021 – by Eric Koons
As extreme weather events multiply, the world is echoing calls for more action to mitigate climate change.
From speeding up the current renewable and sustainable energy transition, making funding more accessible, and finding more opportunities to reduce carbon emissions. Global citizens are asking for more action.
U.S. Special Envoy for Climate John Kerry sums up the growing sentiment well:
“I think there’s a growing sense of urgency, but I don’t think it’s quite at the peak level that needs to be done. We’ve got to reduce emissions significantly enough between 2020 and 2030 that we are able to keep alive the limit on the Earth’s temperature rise.”
With the backdrop of heavy flooding across Europe, wildfires raging throughout Canada, and increasing global temperatures, the need for a faster renewable and sustainable energy transition is apparent.
Scientists are warning that the window to maintain a temperature increase to 1.5°C is closing. This should serve as a major warning bell for governments around the world – especially in Asia.

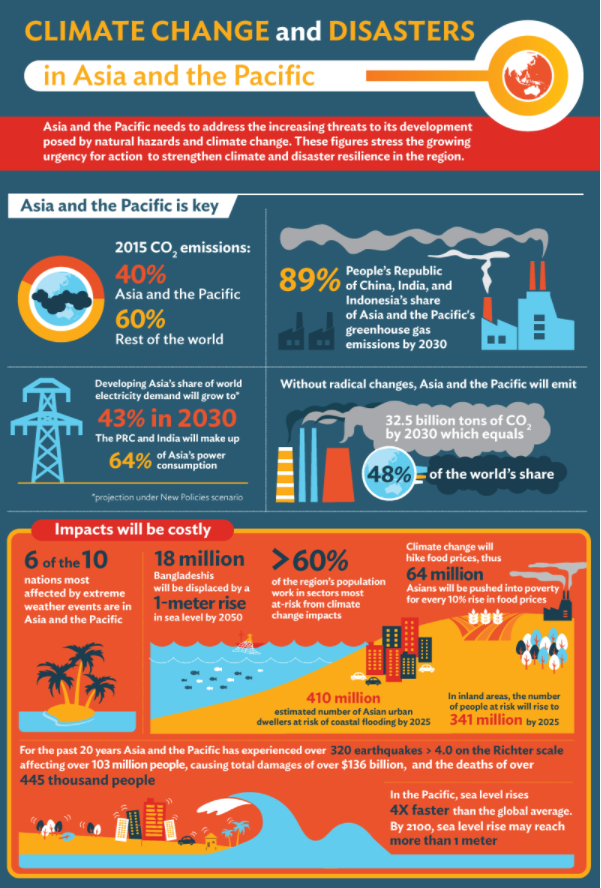
Increased Temperature in Asia
A series of research papers published in Nature (2015) and Science Advances (2017) highlighted how current climate change models predict that heat levels in Asia could rise to fatal levels.
The mixture of humidity, rising temperatures, and more frequent extreme weather events will make living conditions within tropical Asia difficult.
Climate change will have differing effects on nations within the region, some of which we are witnessing. Deadly flooding in China and Bangladesh, rising sea levels in Indonesia, wildfires in Siberia – a renewable and sustainable energy transition isn’t just recommended; it is sorely needed.
The Ups & Downs of Asia’s Renewable Energy Transition
However, as the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) points out, the Asia-Pacific region relies heavily on fossil fuels (85%). So what is being done to ensure a clean energy transition?
Asian Countries Leading the Way
Across Asia, opportunities abound for the implementation of renewable energy.
Major investments are already underway to increase clean energy capacity in the Philippines and Singapore. These investments coincide with commitments to reduce fossil fuel power plants in China. Climate change mitigation has become a key policy issue in India. This has prompted calls for cooperation between Asian nations towards a renewable and sustainable energy transition.
Developing Countries are Falling Behind
Yet, despite all the investments and political negotiations taking place. The region remains far behind the rest of the world in terms of renewable energy.
This is partly due to less-developed Asian countries being unable to garner international energy funding. They rely on their larger neighbours for investments, which often focus on “clean coal” and advanced fossil fuel power plants.
However, these same major economies within the region, on top of investing in renewable energy, continue to build coal power plants.

Asia Will Be a Central Discussion at COP26
This paradox has led to calls for more accountability from Asian countries. We expect this will be a topic of discussion at the United Nations’ yearly climate summit, COP26, later this year. Groups believe COP host-nation, the United Kingdom, is will lobby Asian governments and other laggards to embrace the renewable and sustainable energy transition.
COP26 President Alok Sharma said they want to send a “clear signal to friends worldwide that clean power is the way forward.”
The stakes are steadily rising ahead of COP26 as parties hope to reach ambitious targets on the race to net-zero. This would include a faster transition towards clean energy through more accessible financing, increasing global renewable energy installation, and cooperation between nations to reach the goals.
When considering the impacts that climate change is already having, the need for action is now.
The Renewable and Sustainable Energy Transition Needs Investment
Convincing governments to take more substantial steps towards an energy transition is vital in mitigating climate change.
“The impact of this step will be far greater if we can bring the world with us, and so our desire to support a clean and just energy transition is central to my discussions on the road to COP26.”
Alok Sharma – COP26 President
Renewable energy is the clear investment to make in Asia and abroad. But the question remains whether governments have the willpower to embrace it – because most of the opportunities to transition to a low-carbon economy already exist.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more



