How To Sell Carbon Credits
Source: My Carbon Solutions
23 May 2024 – by Eric Koons Comments (0)
Understanding how to sell carbon credits on the voluntary market is crucial for carbon offset projects. The voluntary carbon market provides a platform for individuals and projects aimed at reducing carbon emissions to contribute to environmental sustainability and potentially profit from their efforts. This incentivises the development of more carbon offset projects.
Carbon credits represent a reduction of one metric ton of carbon dioxide emissions, which can be traded in the market once verified. This market serves as an essential complement to driving private sector decarbonisation with opportunities for companies to offset their greenhouse gas emissions through various projects, including reforestation, renewable energy initiatives and seagrass conservation.
Can You Make Money Selling Carbon Credits?
Selling carbon credits can be financially beneficial. However, because of supply and demand, the voluntary carbon market experiences large fluctuations in credit prices.
Demand typically correlates to three primary drivers: government regulations, international agreements to lower greenhouse gas emissions and corporate sustainability pressures. Supply is influenced by how many credits are on the market, which results from factors including market price and project development cost.
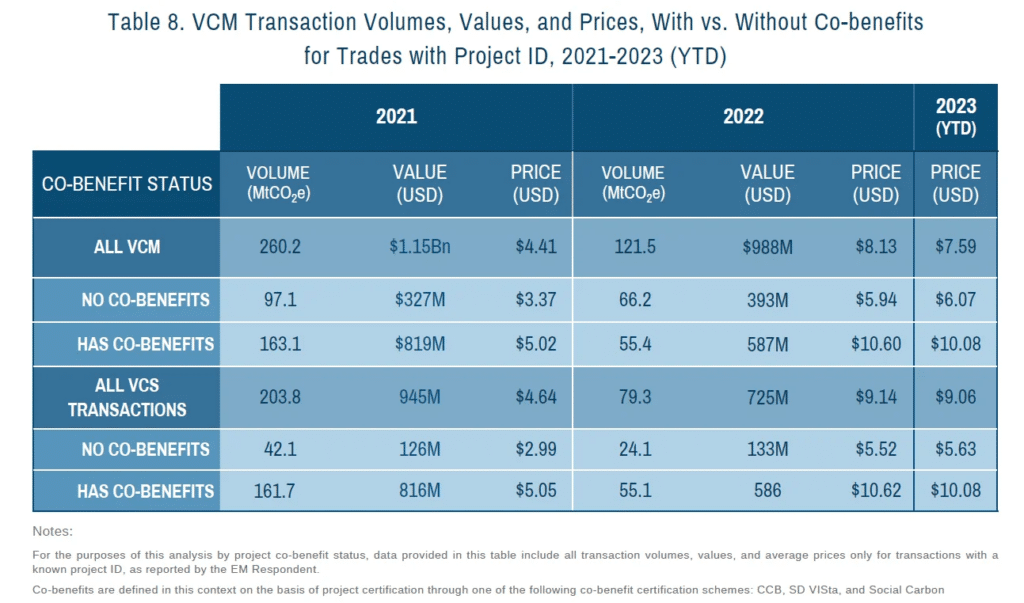
For example, in 2021, the average voluntary market carbon credit price dropped to USD 4.04, but reached USD 7.37 in 2022 – the highest price point since 2008.
Another price factor is the type of project the carbon credit comes from and the quality of the credit. Different types of carbon offset projects have co-benefits, which are often desirable for corporate sustainability strategies. These carbon offsets typically have a higher price.
In 2023, credits with co-benefits were trading at USD 10.08 compared to USD 6.07 for projects with no co-benefits. Furthermore, recent trends show a preference for high-quality, verified credits.
A Successful Carbon Credit Project: Chyulu Hills REDD+ Project
Carbon credit projects can be lucrative when implemented well. The Chyulu Hills REDD+ Project is one example. The project is located on Kenya’s southern border in a region that lacked predictable long-term funding and heavily relied on eco-tourism and donations. Carbon credits were an attractive option to bring more stable income to the area.
The project began verifying carbon credits for forest and biodiversity conservation in 2013 and has now conserved nearly 1 million acres of land, reducing annual emissions by 785,000 tonnes of CO2. The project has generated over 5 million verified carbon credits. The credits provide the co-benefit of social and ecological protection, adding to their value.
The income from the credits is used to fund environmental and social projects in the region, which have created job opportunities for local people, funded schools and developed additional conservation projects.
How Can Carbon Credits Be Sold?
Carbon credits can be lucrative, but selling credits is the last step. There are several key stages to reach that point.
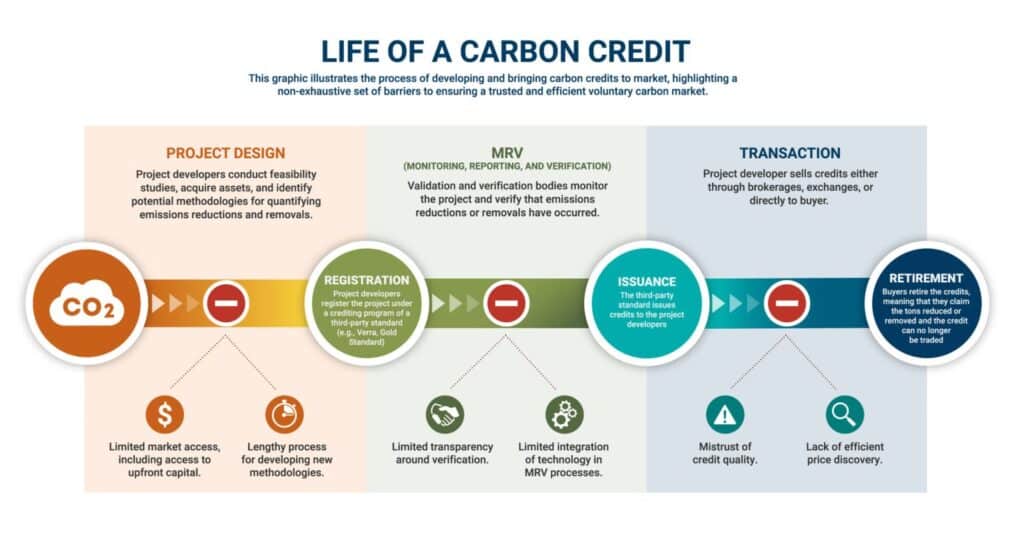
First is project development, which includes planning, implementation and monitoring. Planning and effective monitoring are vital to ensuring that emissions reductions are meaningful. Second is third-party verification through recognised standards such as Verra or The Gold Standard. This ensures credits reduce their stated emissions and is necessary in the voluntary credit market.
Last is listing the credit in the market. There are several options to choose from based on the size of the project and who the intended buyer is.
Where To Sell Carbon Credits
Options for selling carbon credits include:
- Carbon Exchanges provide transparent and broad market access for trading credits.
- Direct Sales allow for direct negotiation and potentially higher prices with businesses seeking to offset their emissions.
- Brokers offer expertise in navigating the market, connecting sellers with buyers and facilitating transactions.
Risks and Returns
The carbon credit market offers significant financial potential but also carries risks, such as regulatory changes and market volatility.
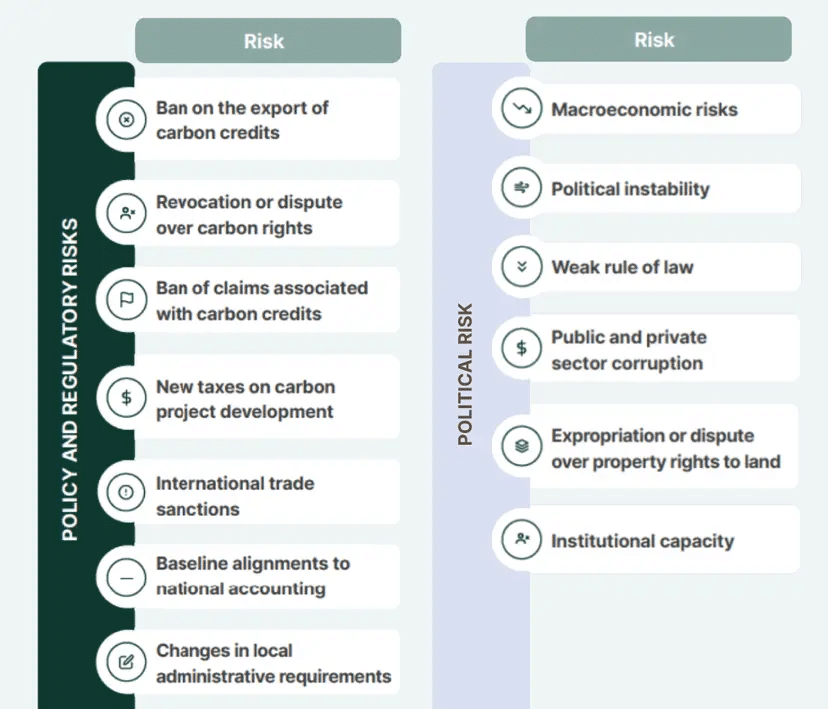
The quality of carbon credits is critical, as lower-quality credits can carry reputational risks and might not effectively contribute to emissions reductions.
High-standard, environmentally impactful projects generally fetch higher prices and enjoy more stable demand. However, these projects typically require stringent planning, oversight and transparency.
Seizing Opportunities in the Voluntary Carbon Markets
The voluntary carbon market presents valuable opportunities for emissions reduction projects and for reducing carbon footprint, particularly in the developing world, where financial incentives can significantly impact local people. Revenues from these projects support both environmental sustainability and regional economic development.
Looking ahead, the market is poised for significant growth due to increasing regulatory support and a commitment to sustainability. Estimates show the carbon credit market will grow at a compound annual growth rate of 38.7% until 2030. There is a major opportunity for groups looking to enter the market and sell carbon offsets.
Stakeholders that enter the market should focus on developing high-quality, verifiable projects that align with global sustainability goals to optimise returns and manage risks.
Carbon Credits Under Scrutiny from Critics
However, carbon credits have faced backlash for several reasons, with critics claiming they don’t do enough to reduce carbon emissions.
- Real reductions: There’s potential for carbon offset projects to merely ‘offset’ climate impacts rather than truly reduce them at the source.
- Transparency: Issues with the accuracy and transparency of measuring and verifying its effectiveness lead to questions about the actual environmental impact of these projects.
- Enabling more pollution: Carbon credits can sometimes allow companies to continue polluting by purchasing credits rather than making genuine efforts to reduce their emissions.
- Complexity: The market for carbon credits can be complex and prone to manipulation, raising doubts about its effectiveness in reducing emissions sustainably.
Investors seeking to use carbon credits to reduce emissions and contribute to climate change mitigation should carefully review such mechanisms before investing.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more








