The Pros and Cons of Ethanol: Does It Have A Place In The Future?
16 February 2023 – by Eric Koons
Ethanol: Pros and Cons
There are many pros and cons of ethanol. As a result, people have debated over ethanol fuel for several decades, particularly regarding its environmental and sustainability impacts.
Proponents of ethanol ethanol argue that it is one of the alternative fuels and it is a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. In contrast, critics argue that it is not a viable solution for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and may contribute to environmental problems.
What Is Ethanol Fuel?
Ethanol fuel is a type of biofuel made from starch or sugar-based crops. The type of crop used varies by country and heavily depends on what grows in the region’s climate. For example, corn is the most common source of ethanol in the United States, and sugar cane is the most common in Brazil. The US and Brazil account for around 81% of the world’s ethanol production.
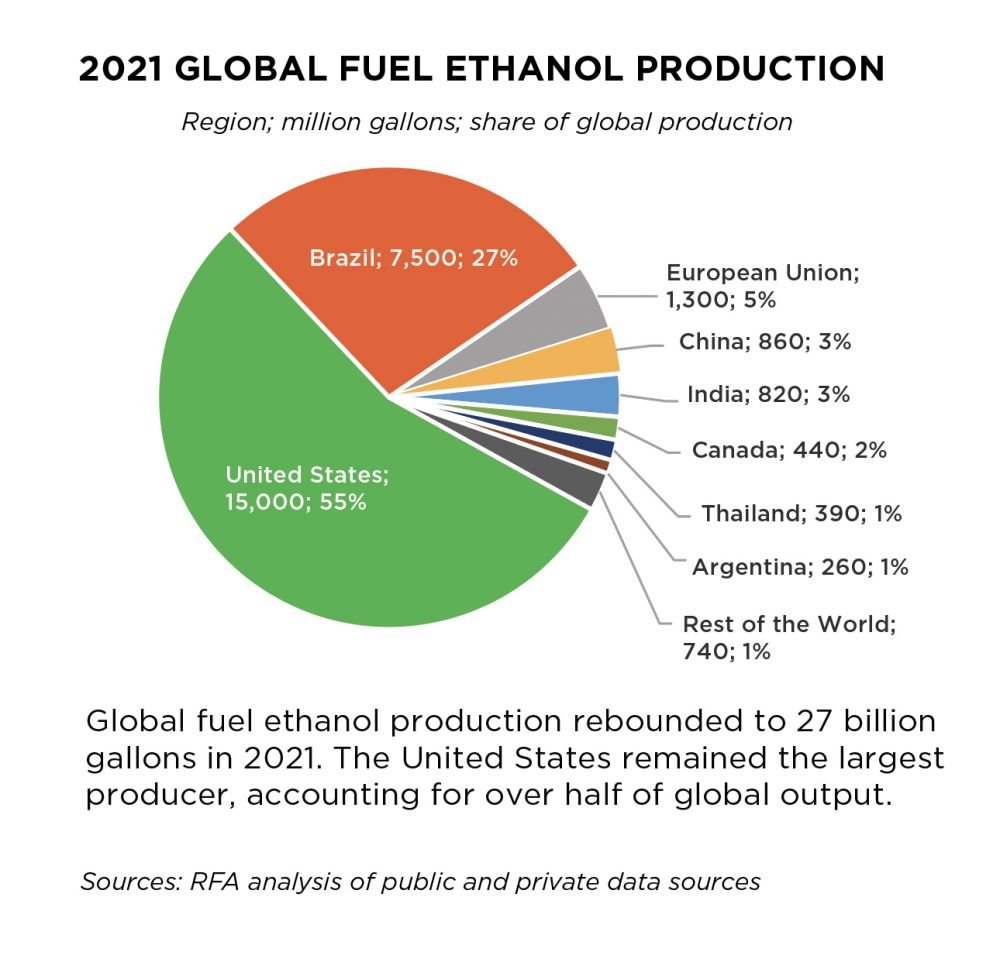
How Is Ethanol Fuel Produced?
Ethanol fuel is produced through the fermentation of starch or sugar-based crops, followed by distillation to make a high-alcohol content liquid. Its primary use is as a fuel additive mixed with gasoline to reduce emissions and improve engine performance. In the US, gasoline typically contains around 10% ethanol.
Here are some advantages and disadvantages of ethanol fuel:
Advantages of Ethanol – Pros
1. Renewable Energy
Ethanol and biofuels come from biomass, a renewable energy source. The crops grown to produce biomass feedstocks harness energy from the sun and grow relatively quickly. During photosynthesis, the plants sequester carbon dioxide, which is eventually released during combustion. This cycle makes the process carbon neutral.
2. Fewer Greenhouse Gas Emissions – Ethanol vs Gasoline
One of the main benefits of all biofuels is that they are significantly less carbon-intensive than traditional fossil fuels. Because ethanol fuel is carbon neutral, the feedstock absorbs carbon to grow, then releases the same amount when burned, and new feedstock is quickly grown to continue to cycle. The only true emissions come from energy inputs from farming practices and transport.
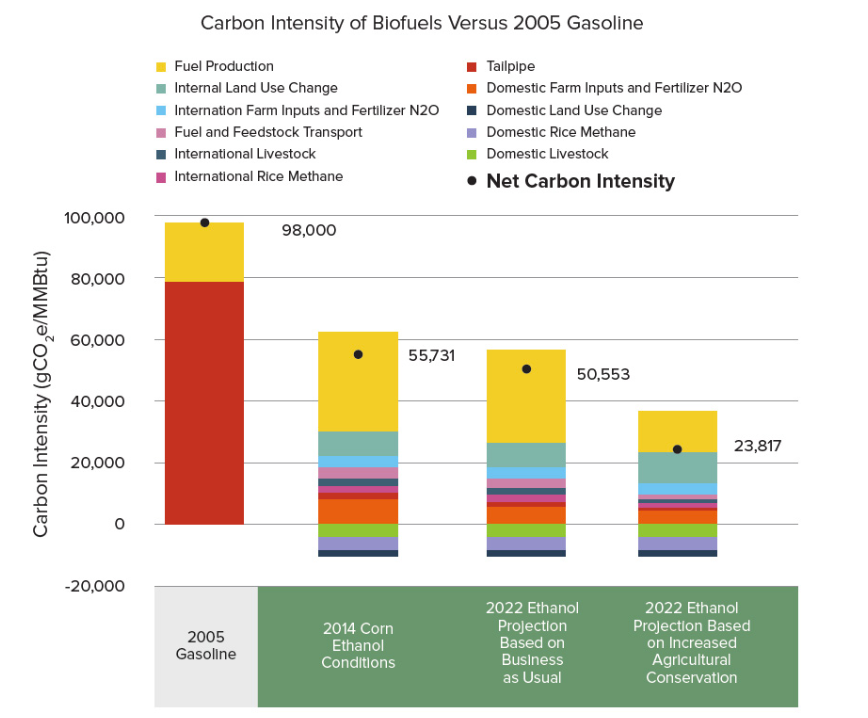
Alternatively, fossil fuels take millions of years to form, so new fossil fuels can’t be quickly produced to offset the carbon released. Additionally, traditional gasoline and diesel fuel require significant energy input to extract, refine and transport long distances. A recent study found that US corn ethanol releases 44-52% fewer gas emissions during its life cycle than gasoline.
3. Ethanol Production Supports Rural Economies
Ethanol fuel production is a major source of income for farmers, particularly in rural areas. This creates employment opportunities in communities that often lack a diversified job market.
Idle or partially employed people are a significant waste of resources for countries. In 2021, the ethanol biofuel industry in the US employed 73,000 people and boosted household income for these employees by USD 28.7 billion.
4. Increased Energy Independence
Countries can reduce their dependence on foreign oil resources by relying on the domestic production of ethanol fuel. This allows nations to develop policies and take actions that make a positive impact.
The Russia-Ukraine war is a recent example of why energy independence is so important in a globalised world. Europe’s dependence on Russian natural gas has shaped Europe-Russia relations and is a major bargaining chip for Russia.
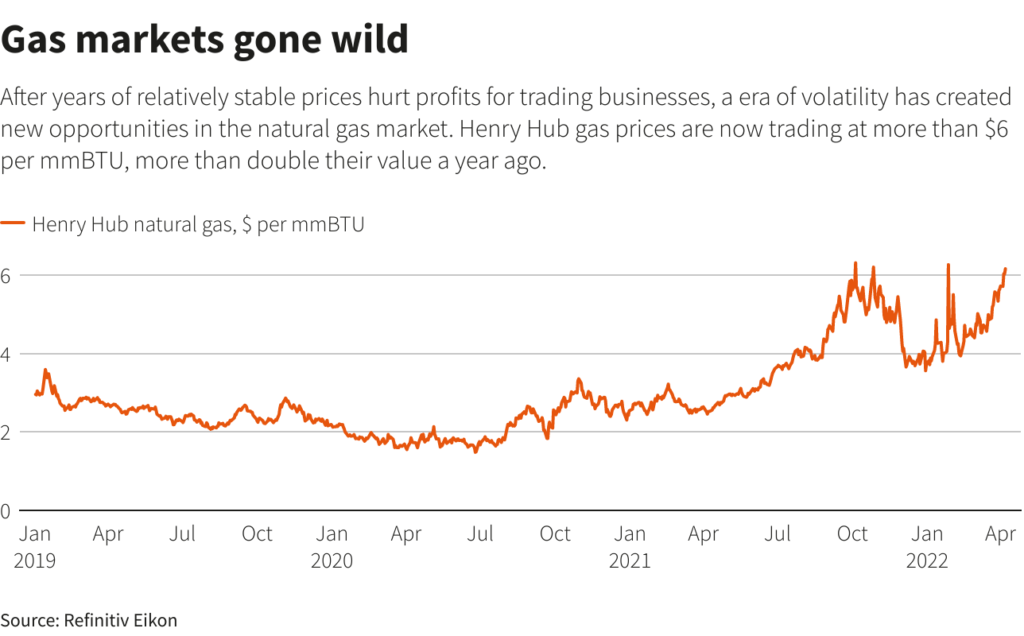
5. Stable Prices
Fossil fuel prices are notoriously volatile because they are a limited resource controlled by a fraction of the world’s countries. For example, 2022 saw record prices for natural gas in India due to the Russia-Ukraine war. Similar effects are occurring around the world, which is leading to global inflation and energy shortages.
Biofuels and other renewables are significantly stabler when it comes to price because they need minimal financial investment after initial construction. Additionally, there is an unlimited supply, and countries can produce them locally from domestically grown crops. This alone is a major pro against the cons of ethanol fuel use.
Disadvantages of Ethanol – Cons
1. Land Use Issues
The production of ethanol feedstock requires large quantities of arable land. Clearing land of native vegetation leads to habitat loss for native species and biodiversity loss. It can also reduce the overall health of surrounding intact ecosystems.
Furthermore, native forests are almost always more efficient at removing and storing carbon than the carbon savings from biofuels. This difference leads to a carbon debt, which one can pay back over time. An excessive carbon debt in the near term will be a hurdle as the world fends off critical climate change tipping points in the next few decades.
2. Water Use
Corn and sugar cane are water-intensive crops, and their use can strain local water supplies. This is particularly relevant to major agricultural areas in the US and Brazil that already have drought issues.
As climate change continues, the world will face growing water stress concerns.
“Agricultural water scarcity is expected to increase in more than 80% of the world’s croplands.”
Earth’s Future
Food Versus Fuel
As existing croplands switch to ethanol production, the available land for food production declines. This leads to increased crop prices, which raises food prices for consumers. This pushes the agricultural sector to clear more native land to support food demand.
Another concern is that the world’s population is steadily increasing, and food demand is increasing. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) predicts that the world will need to produce 70% more food by 2050 to meet the growing population.
Is Ethanol Good for the Environment?
While there are pros to ethanol fuel, there are also significant cons that become more harmful as the world feels the impacts of climate change. Regardless, ethanol has its place in the energy mix and can be a useful component of gasoline as the world transitions away from fossil fuel systems.
However, it is unlikely that ethanol will ever completely replace fossil fuels. Renewable options like electric battery plug-ins and hydrogen vehicles are the main front runners.
In the near term, the selective use of ethanol can be impactful. It requires conscious decisions on where to implement production and how it will impact local and global communities.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more



