The Pros and Cons of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
07 November 2022 – by Eric Koons
There are many pros and cons of hydrogen fuel cells, but the advantages are beginning to outweigh the disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells. However, there is still work to do before they are ready for large-scale adoption. As with many new technologies, the roadblocks primarily relate to cost, infrastructure and regulation.
However, research continually shows that hydrogen fuel cells are needed in the world’s race to net-zero. They produce no direct carbon dioxide emissions and are one of the only viable low-carbon fuel solutions for several types of transportation, like air travel.
What Are Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
Hydrogen fuel cells function on a relatively simple principle. They rely on the fact that hydrogen is highly reactive and forms H2O (water) in the presence of oxygen. As hydrogen and oxygen bond, they release electricity, heat and water vapour. Therefore, this process is the opposite process of water electrolysis, which is the primary way we produce hydrogen.
Hydrogen fuel cells utilise a cathode and anode to create a difference in charge between the hydrogen and oxygen atoms that enter the system. This process is described in the diagram below:
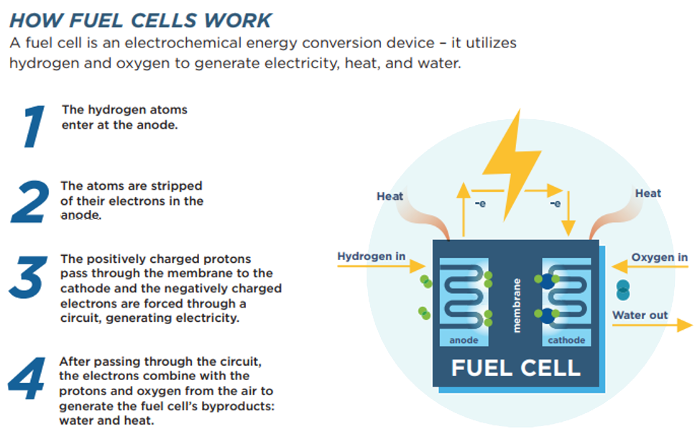
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
One of the main applications of hydrogen fuel cells is replacing the role of batteries in energy storage. Presently, we use batteries in almost all electronics, yet they remain hard to scale up. This scalability issue is one of the main struggles with storing renewable energy. Hydrogen energy is a potential solution to this issue, yet there are still pros and cons of hydrogen power to consider.
What Are the Advantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
Currently, the best commercial battery technology we have is lithium-ion. Lithium-ion batteries have an energy density of about 0.3 MJ/kg – 400 times less than hydrogen. The high energy density of hydrogen is one of its most significant advantages over batteries and fossil fuels.
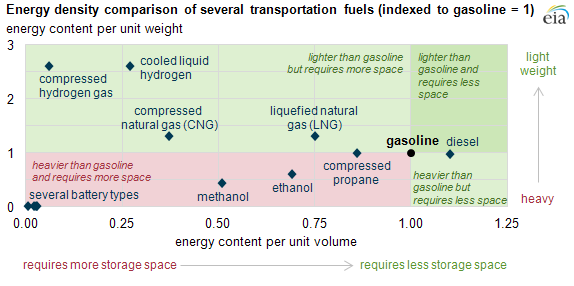
Some other advantages of hydrogen fuel cells include the following:
- Hydrogen is the most common element in nature.
- Hydrogen is an energy carrier. If the energy used to produce it is from renewable energy sources, so is the hydrogen.
- It is twice as efficient as traditional internal combustion engines.
- There are no emissions, resulting in a carbon footprint reduction for both commercial and residential use.
- It can be locally produced.
- Long-term storage is possible.
- Hydrogen doesn’t self-discharge like lithium-ion batteries do.
What Are the Disadvantages of Hydrogen Fuel Cells?
However, as with most other technologies in development, there are also some disadvantages. Among the most prominent is price. As of 2021, Lazard found that the levelised cost to produce hydrogen fuel is more than the fossil fuels it would replace. Lowering the price requires more private-sector investment, higher government subsidies and favourable regulation.
Other disadvantages of hydrogen fuel cells are as follows:
- Hydrogen production is energy intensive.
- Catalyst materials are rare and expensive.
- Hydrogen storage is prone to leaks.
- There is a lack of infrastructure for long-range transport.
- It is highly flammable.
A Look at Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Transportation
The transportation sector is one of the most promising future applications for hydrogen fuel cells. While several hydrogen-powered personal vehicles are currently on the market, the main application will likely be in heavy-duty vehicles and planes.

Both of these modes of transportation are well suited to the use of hydrogen power because they require travel over long distances and are impacted by weight. Hydrogen’s high energy density means that trucks and planes require less fuel to travel the same distance in comparison to standard ICE and battery-powered vehicles.
Less fuel translates to more space for the transporting of goods and better fuel efficiency. Additionally, if they use green hydrogen, they can be carbon neutral – an important milestone for both sectors in the coming decades.
The Future of Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Beyond price, the largest obstacle to expanding hydrogen fuel cell technology is the lack of demand. Generally, this is quite straightforward. If demand increases, the investment will follow, and production costs will drop.
One way of creating this demand is by developing incentives for the private sector to adopt green hydrogen technology. In reality, the needed growth largely hinges on regulatory changes and subsidies that would make it beneficial to conduct research and risk capital on this relatively underutilised technology.
Considering the global efforts underway to decarbonise economies and the scope of work needed to meet climate targets, sustainable hydrogen energy will more than likely become a part of the climate solution. In essence, hydrogen’s versatility and potential for helping to stabilise energy grids, as a low-carbon fuel source, will give it a promising future.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more



