The Surge Of Solar Energy In Pakistan
Source: Dawn
17 April 2025 – by Eric Koons
Solar energy in Pakistan has been gaining traction amid Asia’s fast-paced shift towards renewable energy. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), Asia accounted for over half of the world’s new solar capacity additions in 2023.
The Rise of Solar Solutions
In this context, Pakistan is emerging as a vital market for solar installations. The country imported 22 GW of solar panels in just 2024. While the country’s installed capacity is still relatively low, this import level signals significant solar growth in the next few years. This growth is driven by various factors, including favourable government policies, rising electricity costs and rapidly increasing energy demand.
How Much Solar Energy Is Produced in Pakistan?
Pakistan’s solar sector is booming, yet the total installed capacity remains far below the global average. Specifically, solar energy in Pakistan accounts for just 0.9% of the country’s total electricity supply, which is dominated by gas, hydropower and coal.
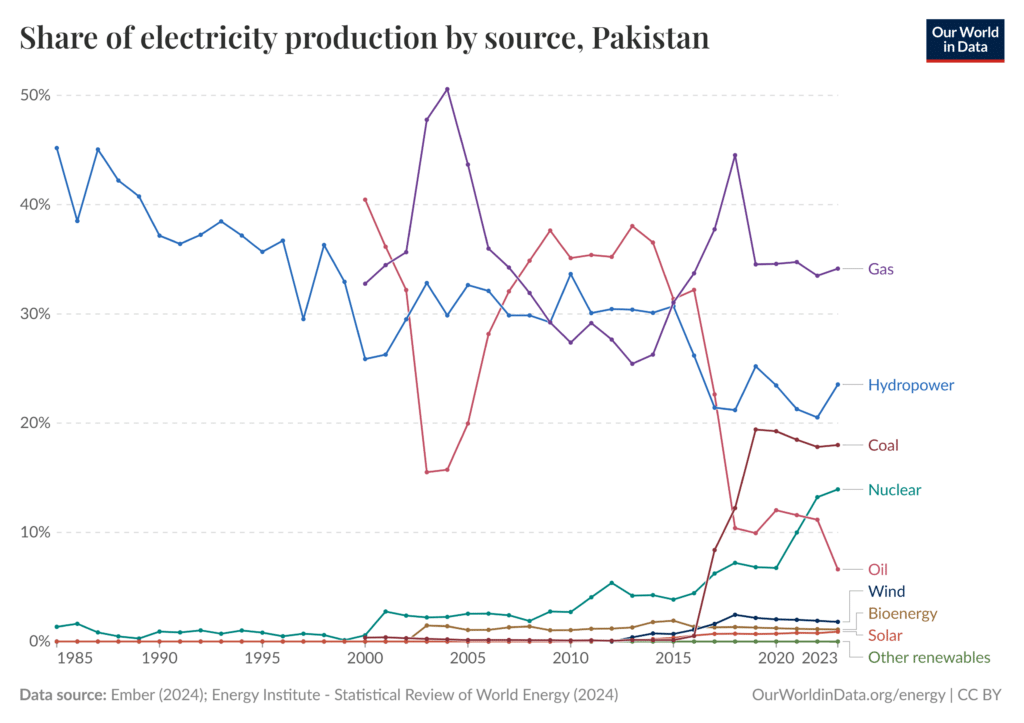
That being said, the country has become one of the world’s largest importers of solar panels and imported the third-most Chinese solar panels in 2024. In fact, Bangladesh imported 50% of its total existing energy capacity (46 GW) in solar panels in 2024. Experts predict the country will continue this trend, driving a massive shift in the country’s energy mix.
Decline in Solar Panel Prices in Pakistan
Interestingly, this is mainly due to demand from private installations, not utility-scale projects. Furthermore, this is largely the result of outside and economic forces, even though the government has played a role. This is primarily due to rapidly declining solar panel costs in tandem with skyrocketing grid electricity prices. Solar power in Pakistan presents a more reliable and cheaper energy source for millions of people in the country. It has become easy for any household or business to install solar panels.
Impact of Supportive Government Policies
While Pakistan has had mixed results in its solar energy policy, recent changes are expediting the country’s existing upward trend of solar power. Notably, the country’s amended net-metering policy allows residential and commercial solar system owners to feed unused electricity back into the national grid. This helps residential and commercial owners offset their energy bills and invest in local, on-site solar systems. This policy has seen massive growth. From June 2023 to December 2024, the on-grid net-metered solar capacity increased from 1.3 GW to 4.1 GW.
To further improve the affordability of solar technology, the government has exempted solar panels, their components and solar system batteries from import taxes. This is a key driver in the spike in Chinese solar panels entering the country, making solar much more attainable for residential owners.
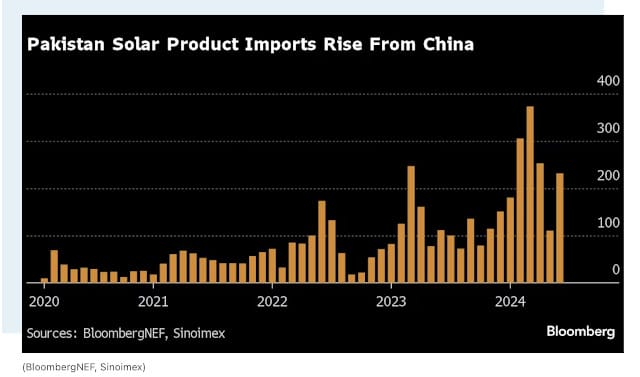
However, challenges remain. Grid capacity limitations pose barriers, as outdated transmission lines can struggle to handle increased feed from intermittent renewable sources. Additionally, the country has largely failed to attract significant foreign investment into the renewable energy ecosystem other than China. These are both key requirements for the long-term growth of the renewable energy sector.
Solar Power in Pakistan: Impact of Adoption
Pakistan’s rapid adoption of solar energy has brought benefits that extend well beyond electricity generation. The renewable energy sector tends to create more jobs per unit of electricity generated than fossil fuels, suggesting that a robust solar market can boost local employment. Technicians, engineers, project managers and maintenance crews are in demand as solar infrastructure expands. The World Bank estimates this will create over 200,000 jobs in the country by 2030.
From a climate perspective, increasing solar capacity is crucial if Pakistan is to achieve its 2030 (60% renewable energy) and 2050 (net-zero) emissions reduction goals. While the country’s overall greenhouse gas emissions are relatively modest on a global scale, it is among the nations most vulnerable to climate change. Without adequately developing the necessary climate adaptation and mitigation measures, this could cost the Pakistani economy USD 1.2 trillion by 2050. This transition also complements efforts to improve air quality and public health in urban centres.
In rural and underserved regions, solar energy projects offer transformative socioeconomic benefits. Off-grid solar systems power schools, health clinics and local businesses, stimulating grassroots development. Over time, these improvements can strengthen community resilience, reduce internal migration to overcrowded cities and foster inclusive economic growth.
Sustaining Pakistan’s Solar Momentum
Looking ahead, Pakistan must take concrete steps to ensure its solar expansion is sustainable. First, upgrading and modernising grid infrastructure will be essential for reliably integrating a higher share of intermittent renewable power. This is a challenge that nearly every country will face and remains one of the main barriers to the global energy transition. Second, attracting diverse foreign and domestic financing beyond just a handful of investors, particularly for local manufacturing, can spur competition, lower costs and increase resilience against currency fluctuations. Third, policy reforms should continue to prioritise net-metering incentives, focus on developing a long-term cohesive renewable energy framework and privatise portions of the energy sector to spur innovation and efficiency in the industry.
For Pakistan, the benefits of a robust renewable energy network include boosting economic diversification, helping mitigate the impacts of climate change and improving energy security and energy independence.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more



