The Economic Benefits Realized from Green Energy Solutions in Asia
Low impact hydropower plays a crucial role in harnessing natural energy with minimal impacts. (Pennsylvania Environmental Council)
18 February 2021 – by Eric Koons
Green energy solutions and renewable energy sources are two terms that are often used interchangeably, yet are subtly different. Green energy represents a subset of renewable energy with the largest environmental benefits. This includes energy sources like: wind, solar, biomass, geothermal, biogas and low-impact hydropower. Other renewable energy technologies, such as large hydropower, have less environmental benefits overall. These fall under the general category of renewable energy sources.
Benefits of green and renewable energy
Both green energy solutions, and renewable energy as a whole, have various economic benefits. Benefits vary by region, but generally include:
- energy security
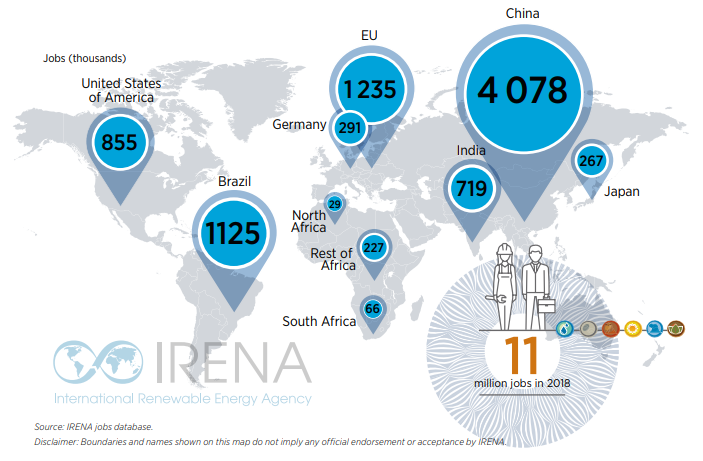
- job creation
- strategic economic positioning
- cheap energy
- externality goals
All of these benefits have incentivized governments to invest in green energy solutions.
Green energy solutions examples
Examples of these types of green energy solutions are found in a variety of Asian countries.
Vietnam’s Feed-In-Tariff
In Vietnam, the Government announced a solar feed-in-tariff (FiT) policy in 2016. This policy encouraged the investment into solar power generation by guaranteeing renewable energy producers an above-market price. This resulted in a rapid increase in solar power capacity. From less than 10 megawatts in June, 2018, to over 6,300 megawatts by September, 2020. Thereby creating the largest solar market in Southeast Asia.
Bangladesh’s Solar Home Systems Initiative
A second example of green energy solutions is the Solar Home Systems (SHS) Initiative facilitated by the government-owned Infrastructure Development Company in Bangladesh. The SHS initiative contributed to the Government’s 2020 target of providing electricity to all citizens. It solved the issue of an aging energy infrastructure and dispersed community obstacles. Launched in 2003, 4.12 million SHS’s had been installed by May, 2017. This provided solar electricity to approximately 12 percent of the entire Bangladeshi population.
In terms of economic incentives, SHS powered households had significant per capita increases in expenditure. SHS powered homes increased food expenditure by 9.3% and nonfood expenditure by 4.7%. This additional spending went directly to businesses, stimulating the economy. Moreover, the SHS initiative contributed towards the local renewable energy industry by creating new jobs and growing manufacturing capabilities (e.g.: solar panels).
Sumba Indonesia’s Green Energy Solutions

A final example of green energy solutions is found on Sumba Island, Indonesia. The push for green energy was launched by Hivos, in collaboration with district, provincial and national governments. A 37-kilowatt micro-hydropower plant, multiple off-grid solar PV systems, 7,000 solar lanterns and 1,000 biogas digesters were deployed throughout the island. These systems were made available for all residents, regardless of income, through various mechanisms (e.g.: co-operative, leasing). The initiative resulted in reduced fuel expenditure for light, increased crop yields, increased income, job creation and new economic opportunities (e.g.: food packaging).
These examples highlight the many economic benefits that can be realized from green energy solutions in Asian countries. However, it is also important to realize that Asian governments will likely continue to play an important role in facilitating these economic benefits. It falls on governments to collaborate with the right types of stakeholders and/or create the right market conditions.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more




