Top 7 Renewable Energy Innovations: Pioneering the Future
Source: Really Good Innovation
19 September 2024 – by Eric Koons
Renewable energy innovations in the ecosystem are critical to ongoing improvements in energy efficiency. These improvements help lower costs and improve renewable energy capabilities, ultimately increasing adoption.
While meeting interim 2030 emissions reduction targets is feasible with existing clean energy technologies, reaching net zero by 2050 hinges on innovations. This is particularly relevant to technologies for hard-to-decarbonise sectors, like heavy industry, which can’t feasibly decarbonise with existing technologies.
Driving innovation in renewables is a core part of many net-zero scenarios. Luckily, innovation is an ongoing process with breakthroughs regularly occurring. Here are the top renewable energy innovations we are keeping our eyes on.
Top Seven Renewable Energy Innovations To Watch in 2025
1. Floating Offshore Wind Farms
One of the most promising advancements in renewable energy is the development of floating offshore wind farms. Unlike traditional offshore wind farms that are anchored to the seabed, floating wind turbines can be placed in deeper waters, where winds are stronger and more consistent.
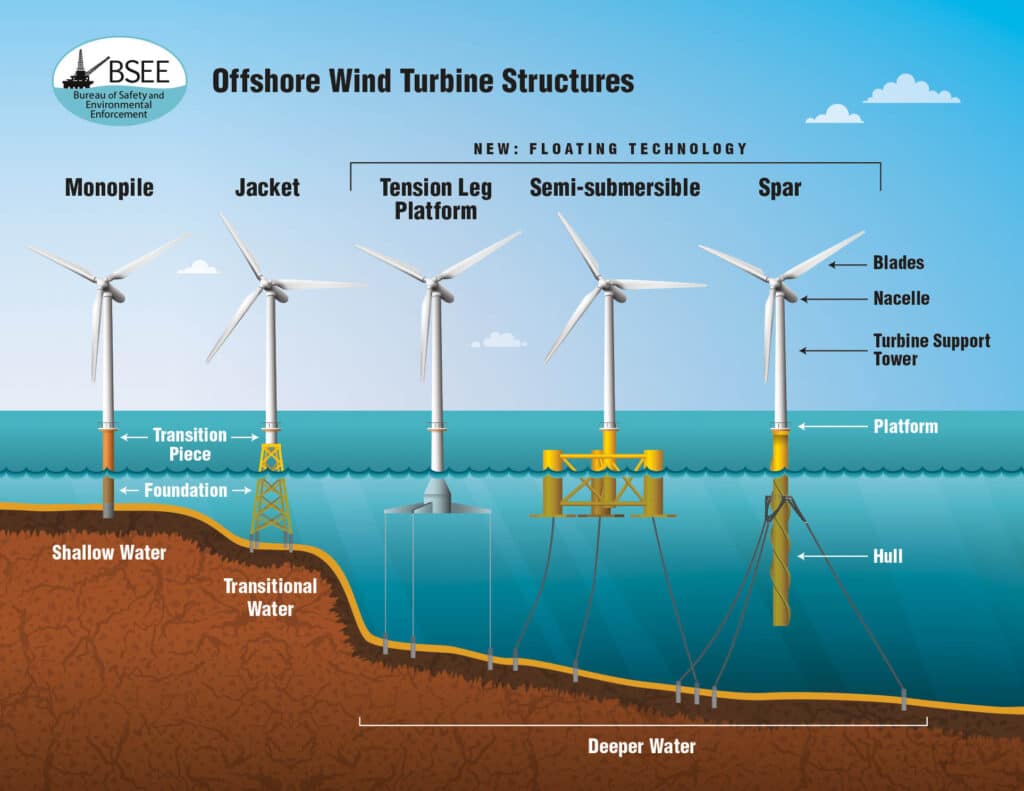
This innovation significantly expands the potential for wind power generation, particularly in regions where the ocean is too deep for conventional turbines. Of the world’s estimated 71,000 GW of offshore wind energy potential, 51,000 GW is only accessible with floating turbines.
However, this technology is still in its early stages, with projects mainly in the feasibility stage. For example, the Hywind Scotland project is a 30 MW floating wind pilot project that has been operational since 2017. The project results are promising, achieving the highest average capacity factor for all offshore wind farms in England every year since development.
This technology will substantially increase global wind energy capacity as it reaches commercial scale.
2. Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Home Energy Storage
As the demand for reliable and sustainable home energy storage solutions grows, hydrogen fuel cells are emerging as a feasible alternative to traditional lithium-ion batteries to store energy. Hydrogen fuel cells offer several advantages, including a longer lifespan and higher energy density. This makes them particularly well-suited for powering homes and small businesses, especially in remote areas with limited grid access.
The hydrogen fuel cell market is currently valued at USD 4 billion yet is set to grow at a CAGR of 25.9% to US 39.86 billion by 2032. This market growth will make hydrogen fuel cells more affordable and available.
3. Enhanced Geothermal Systems
Geothermal energy has long been recognised for its potential to provide a constant and reliable source of renewable electricity. However, traditional geothermal systems are limited to regions with natural geothermal reservoirs to generate power.
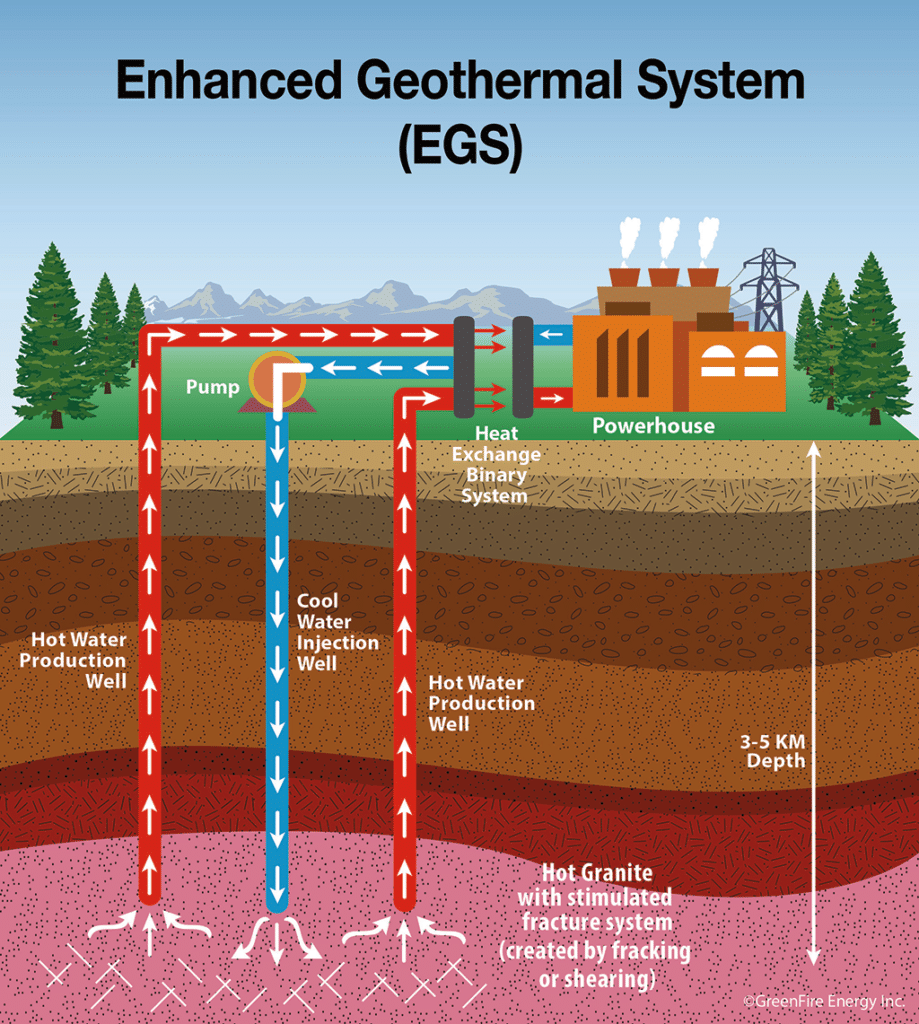
The development of enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) may change this. EGS technology can be deployed in areas without the typical fluids and permeability needed underground for traditional geothermal energy. EGS injects fluids deep into the ground to create an artificial reservoir, harnessing the earth’s natural heat to generate electricity.
According to the US Department of Energy, EGS could provide over 100 GW of power in the United States alone, making it a significant player in the renewable energy mix.
4. Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS)
Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS) is a growing renewable energy innovation. It provides a pathway to store carbon dioxide from plants permanently. BECCS typically burns biomass to produce energy while capturing and storing the carbon dioxide, effectively reducing the carbon footprint to near zero.
The International Energy Association (IEA) considers BECCS a crucial technology for achieving net zero emissions by mid-century. It is the only carbon removal technique that also provides energy. Furthermore, bioenergy can provide high-temperature heat, which is crucial for heavy industries that struggle to decarbonise with standard renewables.
Most BECCS projects are still in the demonstration stage, and only 2 Mt of carbon dioxide is captured by BECCS annually. This must increase to 185 Mt per year to align with the IEA’s 2030 net zero scenario.
5. Tidal Energy Turbines
Tidal energy is one of the most consistent forms of renewable energy because tides are predictable and regularly occurring. Recent and near-term future advancements in tidal turbine technology are expected to drop costs and increase production efficiency. These advancements will allow turbines to capture energy in even lower-velocity tidal flows, increasing the number of viable locations for their deployment. As tidal energy technology advances, its contribution to the global energy mix will grow.
6. Green Hydrogen – Not Produced from Fossil Fuels
Green hydrogen is produced through electrolysis powered by renewable energy and is a promising solution for decarbonising industries and achieving global climate goals. Unlike traditional hydrogen, which is produced from fossil fuels and involves carbon capture, green hydrogen generates no greenhouse gases during production, making it entirely clean. Predictions show that green hydrogen could meet up to 24% of the world’s energy needs by 2050.
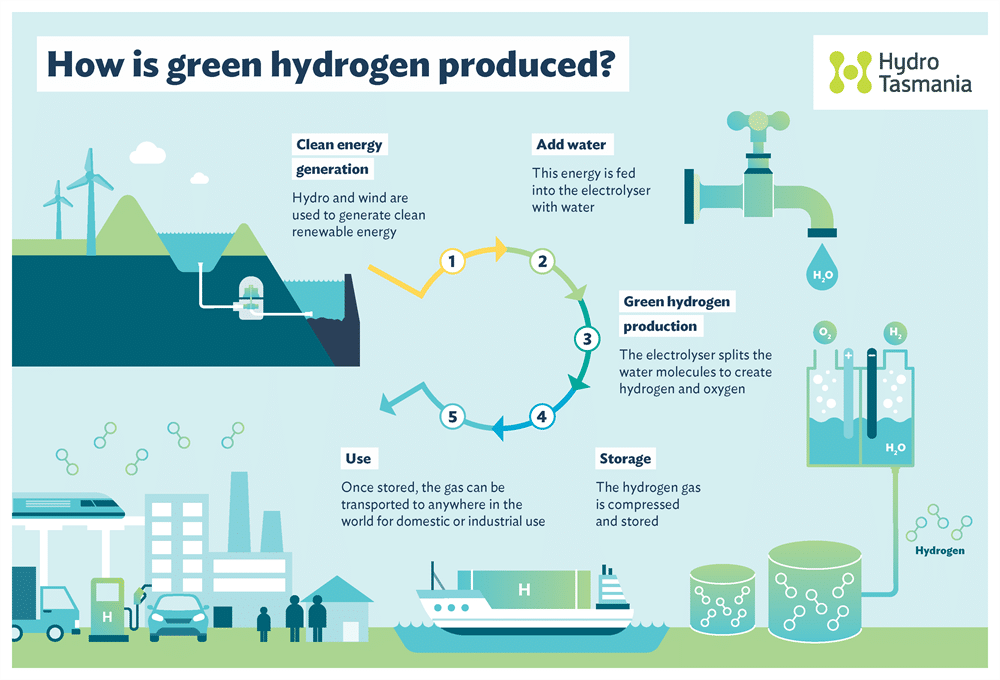
Despite its potential, the cost of producing green hydrogen – currently between USD 3 and USD 8 per kg – remains challenging. However, with technological advances and increased investment, production costs are expected to drop to between USD 1 and USD 2 per kg by 2050. These technological advancements will drive green hydrogen growth.
7. AI For Renewable Energy Sector
Artificial intelligence is revolutionising the renewable energy sector by optimising energy production, improving grid management and predicting demand with unprecedented accuracy. AI algorithms can analyse vast amounts of data from solar panels, wind turbines and energy storage systems to forecast energy generation and optimise performance. For example, Google’s DeepMind has improved wind farm energy output by 20% using AI-powered predictions.
AI also enhances grid efficiency by balancing energy supply and demand in real-time, minimising wastage and reducing costs. AI can revolutionise solar power. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into renewable energy projects and systems will be critical in maximising efficiency and accelerating the global transition to clean energy.
The Role of Innovation in Renewable Energy’s Future
Innovation is essential for meeting global decarbonisation goals, particularly as we aim for net-zero greenhouse gas emissions by 2050. While existing technologies can help achieve interim targets, continued research and development (R&D) investment is crucial.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), annual investment in renewable energy infrastructure needs to triple to over USD 4 trillion by 2030, and this growth will be critical to R&D in the renewable energy sector. Without significant advancements in hard-to-decarbonise sectors, like heavy industry, achieving long-term climate change goals will remain out of reach. Innovation will drive this transition forward.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more







