Solar Renewable Energy Credits and the Energy Transition
Source: Solar Reviews
20 March 2025 – by Eric Koons
Solar renewable energy credits (SRECs) are becoming vital in the world’s rapidly expanding drive toward sustainable power generation. As global solar capacity grows, spurred by government incentives, private sector investments and technological advances, solar renewable energy credits serve as both a financial catalyst and a benchmark for environmental progress. By quantifying the clean energy output of solar installations and allowing owners to trade these environmental attributes, SRECs streamline the integration of renewable power into existing markets.
Understanding Solar Renewable Energy Credits
SRECs represent the environmental attributes of solar energy system and power generation. Project owners typically receive one credit for every megawatt-hour (MWh) of solar electricity produced. This model is recognised in many US states yet is slow to gain traction in other regions. However, many countries have systems that use general renewable energy credits (RECs) in the place of more specific SRECS.
The reason SRECs are so valuable is because they give owners of solar panels an additional revenue channel beyond selling the electricity itself. Meanwhile, regulatory bodies track each credit to maintain transparent compliance with renewable energy targets.
An Opportunity For Asia’s Solar Boom
Asia holds the largest share of global solar capacity with well over 50% of the world’s total installed solar capacity. SRECs are an opportunity for countries in this expanding market to accelerate the energy transition further.
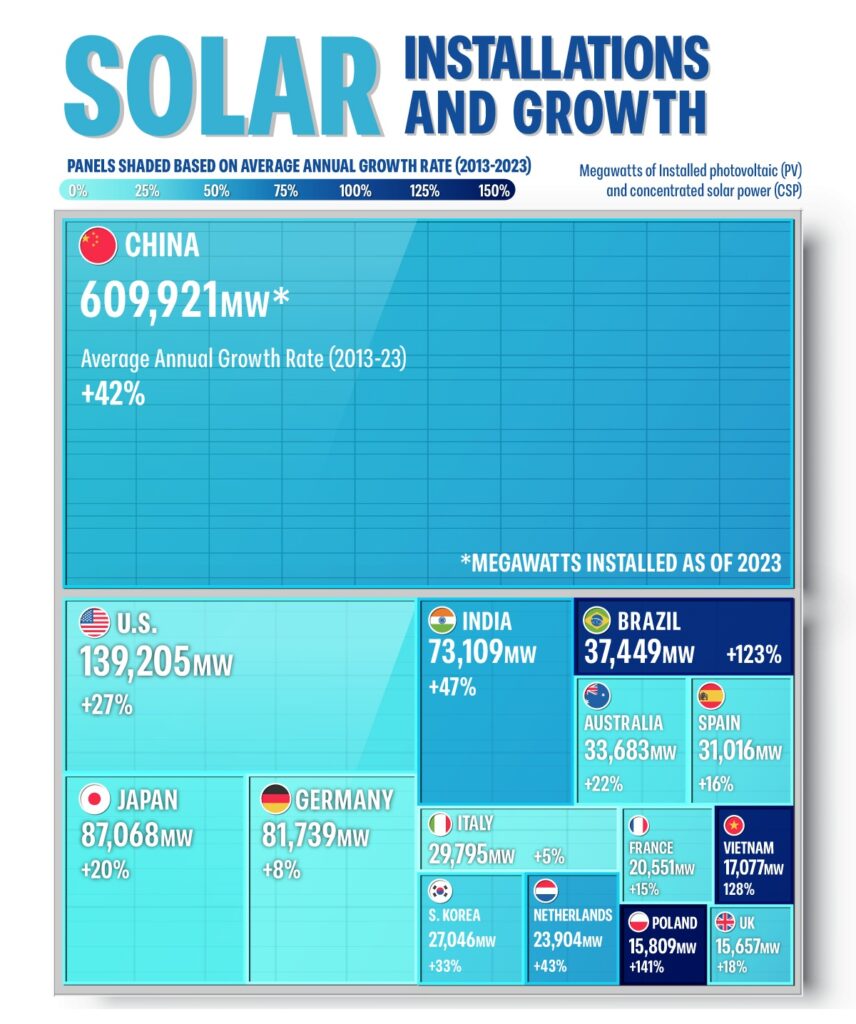
The financial value of SRECs and the environmental benefits of clean power increase the return on investment for solar installations. This, in turn, can accelerate the region’s renewable energy transition and help it meet ambitious national and regional climate targets.
Furthermore, by separating SRECS from standards RECs, governments can target growth in a specific type of renewable energy to align with their long-term energy goals.
What Are the Benefits of Solar Renewable Energy Certificates?
Here are some of the top benefits of solar renewable energy certificates:
Financial Incentives
One of the most attractive aspects of solar renewable energy credits is the additional revenue they provide to solar power producers. In regions with a Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS), utilities are often required to source a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable resources. As a result, this creates a demand for SRECs and RECs.
For example, South Korea’s renewable portfolio standard mandates utilities to incorporate renewables into their supply mix, prompting them to purchase credits. This demand can translate into meaningful revenue streams for solar project owners, as they can sell the electricity generated and the associated credits.
Environmental and Social Impact
By monetising the environmental value of solar energy, SRECs accelerate the global transition to cleaner power sources, reducing both carbon emissions and air pollution. Solar power is the largest source of new power capacity additions worldwide, preventing millions of tonnes of CO₂ emissions annually.
This transition also brings tangible benefits to communities everywhere. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reports that the renewable energy sector employs over 12 million people globally, and the renewable energy market is valued at over USD 1 trillion. This provides major economic benefits for countries around the world. Moreover, as cleaner energy displaces fossil fuel-driven power plants, communities benefit from improved public health, reinforcing the broader social value of transitioning to solar.
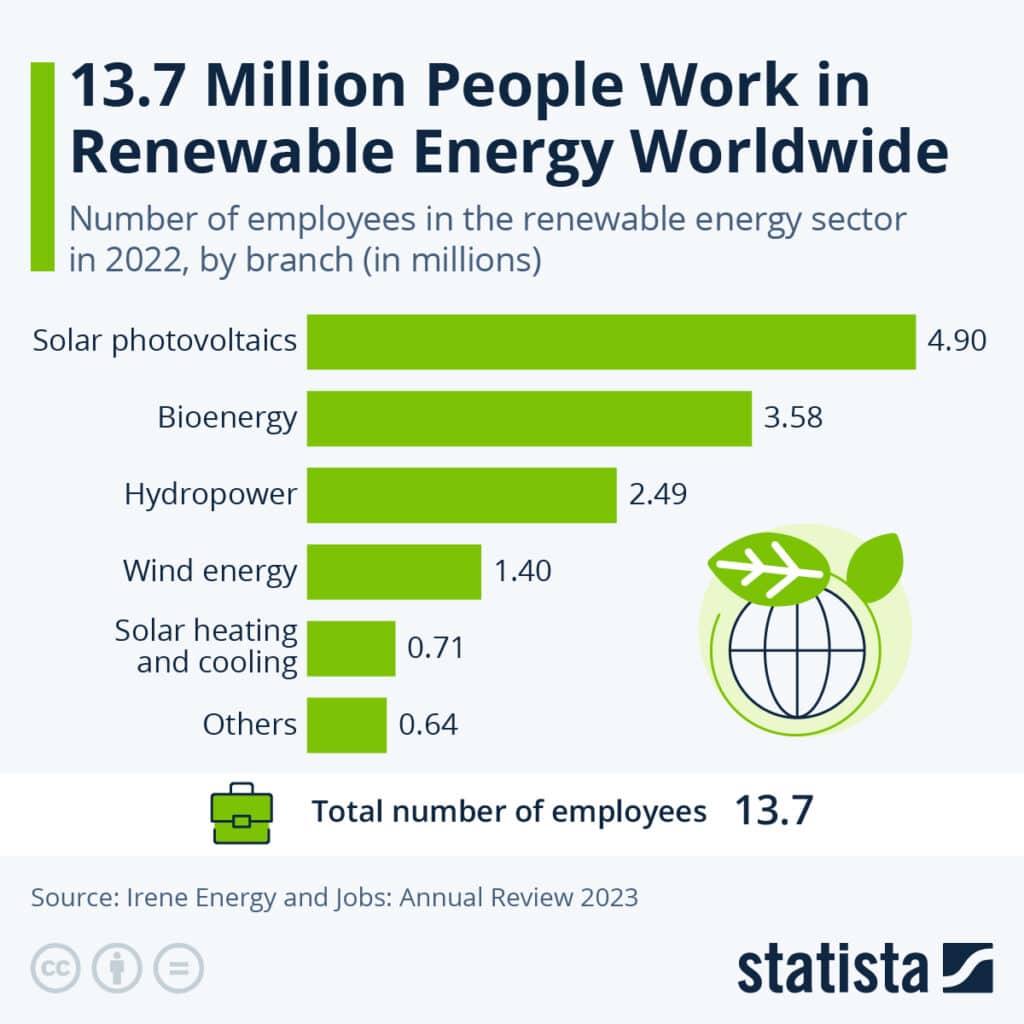
Businesses investing in SRECs can further demonstrate corporate responsibility by aligning with growing consumer and stakeholder demands for sustainable, socially conscious operations.
Market Flexibility and Transparency
Another advantage is the flexibility SRECs bring to renewable energy markets. By separating the environmental attribute of solar power from the actual electricity, these credits can be traded independently.
This setup lowers entry barriers for smaller stakeholders who might not be able to invest in large-scale solar projects directly but still want to participate in the green energy market. Digital platforms that track each SREC from generation to sale also add transparency, making it easier for buyers and sellers to engage confidently.
Challenges and Future Outlook
A key obstacle to widespread SREC adoption is inconsistent policy implementation across countries. Varying definitions of renewable certificates, diverse tracking systems and uneven enforcement can create complexity for multinational stakeholders and local developers alike.
Research from energy consultancies frequently points to the need for standardised regional frameworks, which would reduce complexity and bolster investor confidence. Collaboration among government agencies, utilities and private sector players will be instrumental in creating cohesive, reliable SREC markets.
Technological and Market Evolution
Continual advancements in solar technology, ranging from more efficient photovoltaic panels to scalable energy storage, are making solar power increasingly competitive. At the same time, digital platforms that automate the issuance, tracking and trading of RECs add to the attractiveness of these markets. Some initiatives even involve blockchain-based systems to ensure the authenticity and traceability of each credit. These technological leaps will likely make RECs more accessible and user-friendly, drawing in a broader range of participants.
Projected Growth
Looking ahead, the world’s solar expansion shows no signs of slowing. Projections from the IEA suggest that global solar capacity could double within the next few years as countries strive to meet growing electricity demands through cleaner sources.
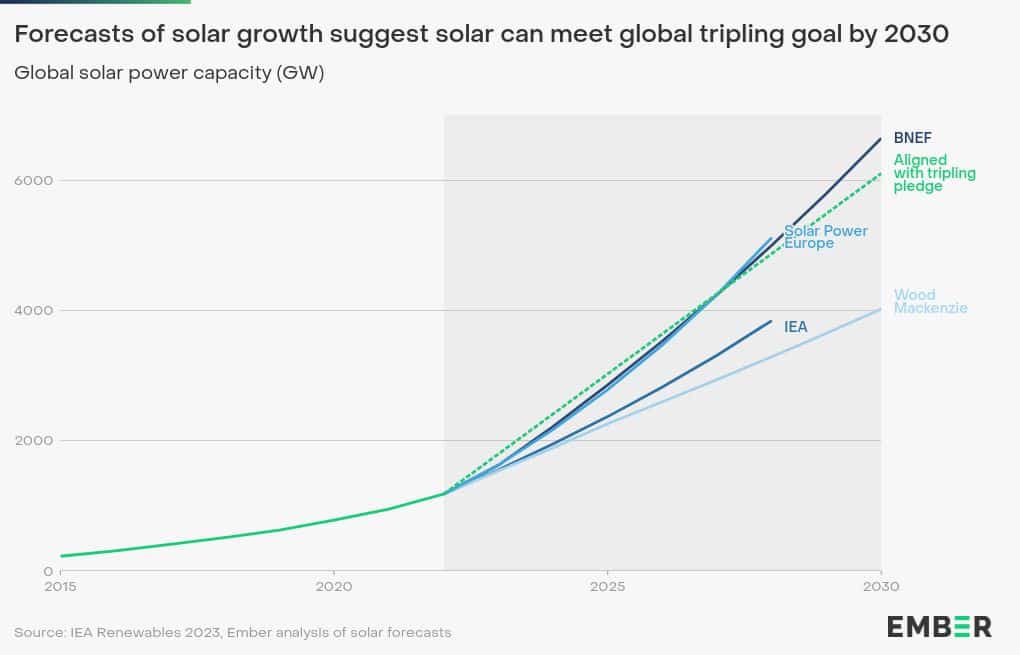
There is a similar momentum behind renewables, thanks in part to corporate net-zero pledges and declining costs. In this environment, SRECs will likely gain increasing significance, serving as both a policy compliance tool and a revenue stream for project owners.
A Path Forward for Solar Renewable Energy Credits
SRECs play a pivotal role in monetising the environmental benefits of solar power generation, particularly in Asia, where solar capacity growth is skyrocketing. By creating a robust revenue model, these credits incentivise the adoption of clean energy solutions, help quantify carbon reductions and provide market-based flexibility for investors and utilities.
Amid diverse regulatory environments, RECs and SRECS have the potential to unify renewable energy efforts across the world, promoting both financial returns and tangible environmental gains. Policymakers, financial institutions and corporate leaders can help shape this burgeoning market by advocating more transparent regulations and supporting emerging technologies that streamline credit tracking.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more