The Corporate Hunt for Renewable Energy Investment
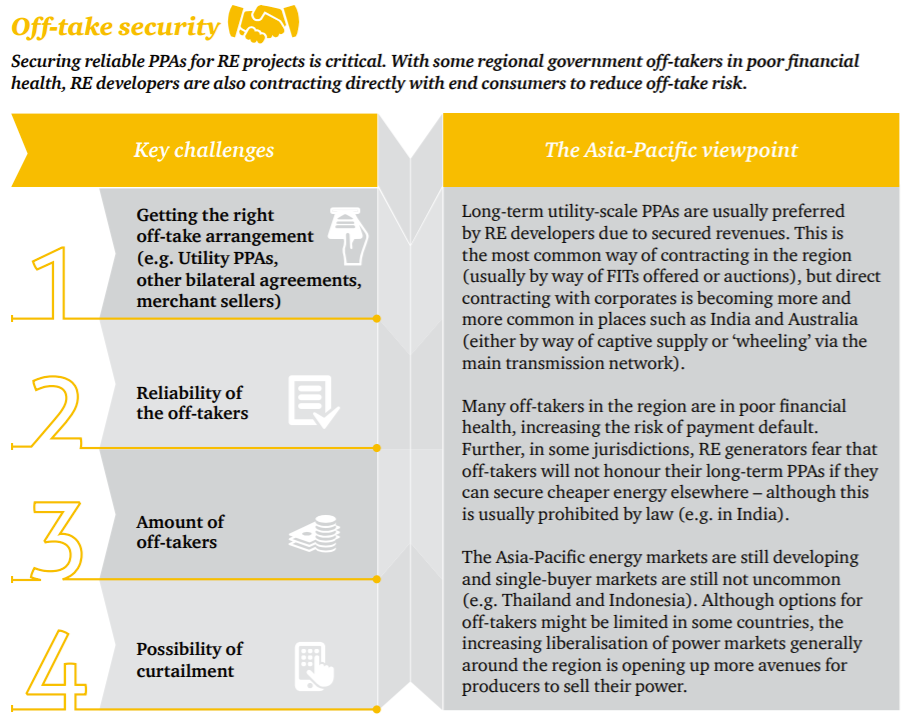
Google matches 100% of its electricity consumption with renewable energy.
12 May 2021 – by Eric Koons Comments (0)
Large corporations can be powerful drivers for change. This is becoming more and more evident in the global transition to renewable energy. In Europe and the US, many corporations including Google, and Facebook have made a commitment to 100% renewable energy. Google achieved this goal in 2017 and made renewable energy investments totaling 2.6 GW to do it. That’s about 1% of the entire renewable energy output in the US! (~ 260 GW). Other corporations such as Amazon, Microsoft, Ikea and Apple are following Google’s lead.
So how about Asia? Are Asian corporates matching the same drive for change into renewable energy investment as thier US counterparts? And if the Asian corporate juggernaut is awakening, what does this mean for clean energy investment? Is there even enough potential capacity to feed this new demand?
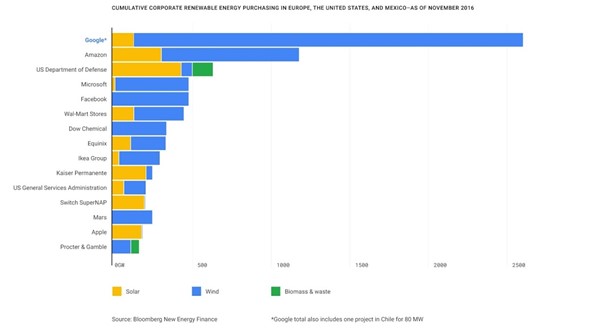
Energy Demand by Corporations
Corporate demand for renewable energy has increased dramatically since 2013. This demand has been driven by US-based corporations. The figure below shows global corporate power purchase agreements (PPAs) by region. In 2019, the US stood at 15.7 GW, with Europe 2.6 GW and the Asia-Pacific region at about 1 GW.
So how much scope is there for corporate clean energy investment in Asia? In 2020, energy use from the industrial sector in Asia was about 30,500 terawatt-hours. To put this amount of energy in perspective, the total amount of renewable energy produced in Asia in 2019 was only approximately 3000 terawatt-hours. Therefore, if all corporations in Asia decided to go 100% renewable, this would drive a ten-fold increase in renewable energy demand.
How do Asian Corporations Change to Clean Energy?
First, buying clean energy requires clean energy to be available and a transmission network for corporations to access it.
Clean energy investments in Asia face several challenges:
- Finance
- Land procurement
- Grid connectivity and stability
- Regulatory and legal frameworks
- Off-take security
Of these, corporations have the most power to fix off-take security by utilizing long term PPA’s. PPAs have become the dominant mechanism by which corporations can access renewable energy investment. Of course, since the electricity must travel through the grid, PPAs must operate within local regulatory and legal frameworks.
A recent study by the RE100 group has found that Australia, China, Indonesia, Japan, Singapore, South Korea, and Taiwan are among the 10 most difficult countries for clean energy procurement. These are all in the Asia-Pacific region. Private sector investment can drive the change, but governments play a crucial role by improving grid infrastructure, energy sources and providing positive regulatory frameworks.
For some countries, like Singapore, they have the problem of simply not having enough land available. Google’s Singapore-based data centers use more power than is produced by Singapore’s entire renewable energy sector. Ventures like the Suncable project in Australia, which plans to send solar energy power to Singapore via an underground and undersea cable, can hopefully help corporations in countries with low renewable energy resources access sufficient clean energy.
Samsung’s Renewable Energy Investments
While overall Asian corporate use of renewable energy is low, Samsung is making significant strides in clean energy procurement. In June 2018, Samsung announced it would work towards sourcing 100% of its global energy needs from renewables. And in 2020 Samsung achieved this goal.
Samsung is also expanding renewable energy investment at home in South Korea. They recently installed solar energy and geothermal facilities throughout the country. Hopefully, Samsung can continue to increase its use of renewable energy and become an example for the rest of corporate Asia.
Opportunity for Clean Energy in Asia
Companies like Google, Facebook, Samsung and a host of others are showing how corporations can play a major role in driving the change to renewable energy. Asian corporations are active, however at present they are only sourcing a small amount of their energy from renewable energy sources. Thus, there are huge opportunities in Asia for renewable energy investment that can be well underpinned by long-term corporate PPAs.
As the cost of renewable energy falls, corporations can gain significant benefits and long-term price security by changing to renewable energy. And at the same time this will boost their environmental credentials. There are massive opportunities for investors, including energy companies, to build renewable energy capacity to meet this demand.
Corporate energy finance projects for renewable energy investment not only allow companies to source cost-efficient and sustainable means of generating power but it also facilitates the deviation away from fossil fuel based power plants and polluting sources of power, which will provide a better outlook for climate change.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more