Asia’s Lower LNG Demand in 2022 Highlights Challenges for Industry Growth
CRS PHOTO / Shutterstock.com
23 January 2023 – by Sam Reynolds
For years, the liquefied natural gas (LNG) industry has assumed that Asia would be a reliable, rapidly growing customer.
But a turbulent year in global gas markets has called this assumption into question. Europe’s push to replace Russian piped gas with LNG caused prices to hit record levels in 2022. In response, demand for LNG in Asia dipped 7%, the first annual drop since 2015. As unaffordable prices stifled Asian demand, utility profits waned, proposed import projects stalled, and countries grappled with a constant threat of fuel shortages and blackouts.
For countries planning to increase the share of LNG in their energy mix, the lessons of 2022 should be a harbinger of challenges to come. If volatile prices and unreliable supplies continue to alienate key Asian markets, the region’s LNG demand is unlikely to grow as rapidly as industry players expect.
Taking Stock of LNG Demand Destruction in Asia
LNG prices in Asian spot markets averaged US$34 per million British thermal unit (MMBtu) in 2022, more than double the annual average in 2021.
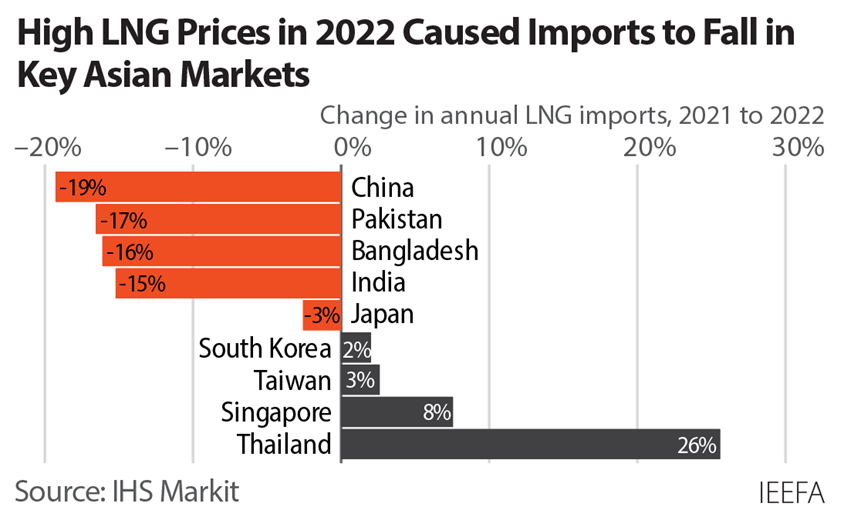
Consequently, Asian LNG demand fell from 270 million tons (mt) in 2021 to 250 mt in 2022, according to data from IHS Markit. The largest drop was in China, where LNG imports collapsed 19% year-on-year due to persistent COVID-related lockdowns and high prices.
As a result, Japan reclaimed its spot as the world’s largest LNG buyer in 2022 despite a decline in LNG imports. The country has accelerated efforts to restart its nuclear fleet, to reduce exposure to volatile gas markets.
South Asia was arguably the hardest hit by high prices. In Pakistan and Bangladesh, an inability to afford LNG cargoes resulted in gas and power shortages, stunting economic growth in key sectors and straining critical foreign exchange reserves. Suppliers to Pakistan and India repeatedly defaulted on long-term contracts, forcing buyers into expensive spot markets or causing them to forego cargoes altogether.
Asia’s imports from LNG spot markets collapsed 17% in 2022. If prices remain volatile in 2023, buyers may continue to limit spot purchases and instead aim to sign new long-term contracts. But with reportedly no long-term contracts available offering deliveries before 2026, incremental LNG demand growth may be a slow burn.
Utilities in Asia Are Feeling the Pain of Higher Fuel Prices
In the wake of the Russia-Ukraine crisis, governments in Asia often attempted to mitigate the inflationary impacts of higher fuel prices by capping end-user gas and power prices. As a result, higher input costs ended up on the income statements of private and state-owned utilities, harming financial performance.
In South Korea, the government refrained from significantly increasing power prices last year to ease inflation. But due to dramatic increases in fuel costs, losses at the state-owned Korea Electric Power Corporation (KEPCO) skyrocketed and are expected to exceed US$24 billion for 2022. To mitigate losses, the government raised power prices 9.5% for the first quarter of 2023, the highest increase in 40 years.
Government regulations in Japan cap the amount that power utilities can increase household electricity rates. As a result, nine out of the 10 largest power utilities in the country experienced significant net income losses in the first half of the fiscal year. JERA, one of the world’s largest LNG buyers, posted a net income loss of US$995 million over the same period and expects to remain in the red for the rest of the fiscal year.
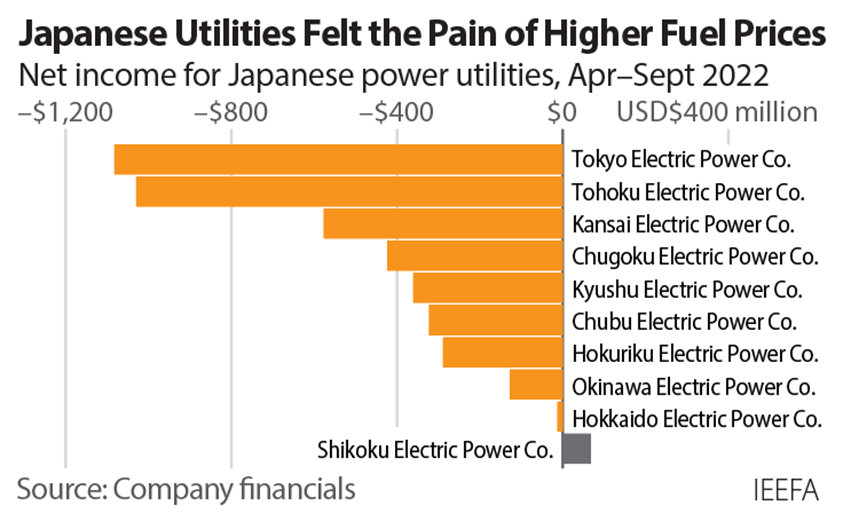
Thailand required state-run electrical utility EGAT to cap power prices in September 2021, incurring a financial burden of US$1.73 billion through April 2022 and US$3.17 billion from May to August 2022.
For countries aiming to enter LNG markets, these issues foreshadow challenges to come. Although the Philippines does not currently import LNG, domestic utility SMC Global Power reported US$275 million in losses at two power plants due to high imported coal and domestic gas costs (linked to global oil prices). The company has also proposed over 36.5 million tons per year of new LNG import capacity, which, if built, would dramatically increase its exposure to volatile LNG prices.
Volatility Muddies the Outlook for LNG in Asia
A recent dip in LNG prices due to warm weather in Europe is welcome news for importing countries. But prices in Asia are still double the previous five-year average of US$14/MMBtu, and analysts expect prices to stay elevated in 2023.
Should prices remain volatile, importers may increasingly seek to minimise LNG consumption, hurting the LNG industry’s long-term growth prospects. Instead, many countries in Asia have accelerated the deployment of low-cost, domestic renewable energy. Key LNG growth markets like India and the Philippines, for example, have announced higher renewable energy targets to limit dependence on global gas markets.
2022 showed clearly that volatility in international fossil fuel markets can have extremely destabilizing impacts on energy security and economic growth. While no one can predict exactly how LNG prices will fluctuate, countries can limit their exposure to uncertain fuel prices by boosting renewables and energy storage technologies.
After all, history is a guide, not a fortune teller.
Sam Reynolds, an energy finance analyst with the Institute for Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA), focuses on the economic, financial, and climate risks associated with natural gas and liquefied natural gas (LNG) infrastructure developments in emerging Asia.
–
This article was originally published by The Institute of Energy Economics and Financial Analysis (IEEFA) and reused with permission.





