Carbon Capture Technology And How It Works
Source: Vox
11 June 2024 – by Eric Koons
Carbon capture technology provides a ray of hope in the world’s mission to achieve the Paris Agreement’s climate targets and limit the effects of global warming.
Global energy demand is taking its toll on the environment, and fossil fuels such as oil and natural gas remain the most common energy source.
Renewable energy is a clean alternative, and while its use is rapidly increasing, the world is not yet at mass adoption. While this transition takes place, we need something to reduce the negative impact that fossil fuel energy from fossil fuel power plants has on our atmosphere.
Therefore, carbon capture technology is a solution that is worth mentioning. The ability to capture carbon emissions before they enter the atmosphere might help us put the lid on carbon emissions until renewables are ready to take over. This captured carbon dioxide through CO2 capture technology can be re-used in industrial processes.
What is Carbon Capture Technology?
Carbon capture technology reduces carbon emissions during this process. It separates the carbon dioxide, which is then captured, transported and stored. The process dramatically reduces the negative effect of burning fossil fuels. However, it isn’t possible to capture 100% of the carbon emissions in most cases.
Burning fossil fuels in power generation produces carbon dioxide as a byproduct. This CO2 enters the atmosphere, contributing extensively to the overall warming of the Earth.
This technology uses different carbon capture techniques and carbon capture methods to work.
Types of Carbon Capture and Storage Technologies:
There are three main types of carbon capture technologies: pre-combustion capture, post-combustion capture and oxyfuel combustion carbon dioxide capture technology.
How Does Carbon Capture Technology Work?
Let’s explore the ins and outs of the three main types of carbon capture technologies.
Pre-Combustion Capture
In pre-combustion capture technology, heat splits the fuel before combustion into a mixture of hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide. The hydrogen can be isolated and burned to produce energy without releasing any CO2.
This allows the capture, compression and transport of the remaining CO2.
This process is a little more complicated than post-combustion capture, making it difficult to retrofit existing power plants with the technology. Pre-combustion capture requires the installation to take place during the construction of a new power plant. Pre-combustion capture is, however, less energy-intensive than post-combustion.
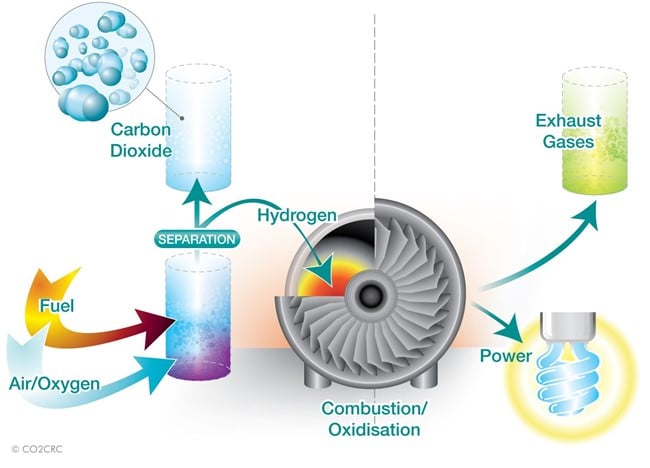
Post-Combustion Capture
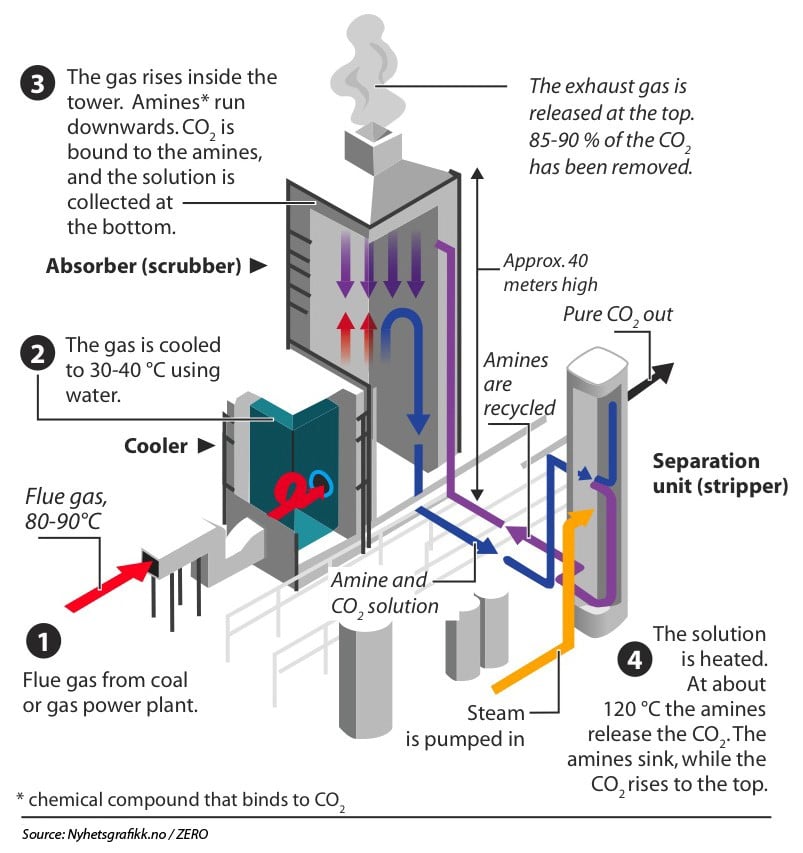
As the name suggests, post-combustion capture sequesters carbon after the combustion process. The exhaust gases from fuel combustion are captured, and the CO2 is separated using a liquid solvent. The CO2 binds with the solvent, and the solvent-carbon dioxide mixture goes into a separation unit. In the separation unit, the CO2 and solvent split. This allows the transportation, storage and utilisation of the remaining CO2. This stored carbon dioxide at the storage site can be re-used.
Post-combustion capture is the most common carbon capture method. The technology can also be retrofitted to existing power plants. As with pre-combustion capture, this method can capture about 90% of carbon dioxide emissions. Post-combustion capture is more energy-intensive than pre-combustion capture, reducing the overall emissions reduction.
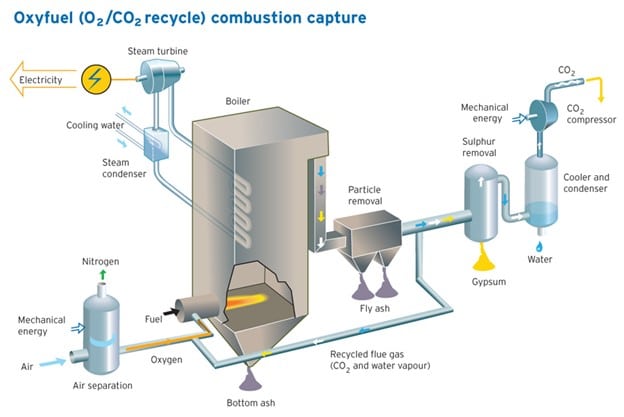
Oxyfuel Combustion Capture – Best Carbon Capture Technology
Oxyfuel combustion capture is the most efficient carbon capture technology, with the ability to capture 100% of carbon emissions. The efficiency comes with a price, however. Oxyfuel capture is the most expensive method of carbon capture and is very energy-intensive.
In oxyfuel combustion capture, pure oxygen is first separated from the air. The pure oxygen is then used to burn the fuel, generating carbon dioxide and water byproducts. Through a condensation unit, the water separates, allowing for the capture of the remaining carbon dioxide.
What Are Some of the Largest Carbon Capture Technology Companies?
Due to the urgency of our climate crisis, several companies are taking advantage of the current situation by trying to help our planet to fight climate change while also making a profit.
Some of the largest carbon capture companies include:
- Carbfix – Iceland
- Global Thermostat – the US
- CO2 Solutions by SAIPEM – Canada
- Net Power – the US
- Quest by Shell – Canada
Who Is the Leader in Carbon Capture Technology?
The leader of the carbon capture debate might be a matter of opinion. Many carbon capture companies want the title, but only a couple can lay legitimate claims.
Quest by Shell captures more carbon than any project of its kind. After learning some lessons from the Quest project, Shell Canada President Michael Crothers suggests that a similar project built today would cost about 20%-30% less to operate.
Carbfix has an intuitive, natural weathering process to permanently store CO2 as rock beneath the Earth’s surface. The company has demonstrated its strategy to be secure, cost-effective and harmless to the environment.
Global Thermostat (GT) finds its competitive advantage in the way it can retrofit an existing plant with carbon capture technology. As a result, GT’s low-cost solutions can be retrofitted to most facilities with as little as one day of plant inactivity.
Carbon Capture is a Potential Short-Term Solution
Renewable energy still needs time for its development and global adoption. Some costs still remain high, especially due to current supply chain issues, compared to fossil fuels. Although the costs are decreasing, the market needs some time to stabilise. The advancement of technology, government subsidies and carbon taxes on dirty energy are speeding up the adoption of renewable energy toward full-scale implementation. In the meantime, carbon capture technology is a potentially viable way to reduce the adverse effects of fossil fuel energy generation.
This article is part of our carbon capture guide.
We will discuss more related topics in the following articles, such as the top carbon capture stocks to invest.

by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more








