Countries Gearing Toward the Clean Energy Transition
04 November 2021 – by Viktor Tachev
This clean energy article tells which countries of Asia give more importance to renewable energy and a clean energy transition.
Not only is Asia the world’s most populous region, but it is also home to two of the top three major emitters of CO2 globally. Part of this reason is that it is the fastest-growing region of the world’s economy and an industrial powerhouse pumping out goods and services for the world. Asia’s place in the global clean energy transition could not be more critical. What Asia should consider more is energy efficiency.
What International Renewable Energy Agency says about Energy Consumption?
According to international renewable energy agency, in Asia and Pacific, 85% of energy consumption is coming from fossil fuels. That’s an alarming situation, which demands great efforts from public and private sectors toward clean energy transition.
Report of International Energy Agency
IEA on 9 June 2021, in a press release, issued a report in collaboration with World Economic Forum and and World Bank and emphasized that, in emerging and developing economies, clean energy investment should be increased “by more than seven times by 2030.” It also highlighted the importance of net-zero emissions.
Asia’s Clean Energy and Renewable Energy Leaders and Regional Development
In every Asian country, there is a clean energy investment story. As a whole, the continent is leading in selling low-carbon goods and services per unit of GDP. This is also on top of accounting for 50% of renewable energy investment globally.
While developed nations like Singapore and Japan are pursuing ambitious net-zero targets, experts note that developing markets will be the growth engines of the clean energy transition. Countries should invest more in solar energy, solar panels, wind energy, green hydrogen, and energy efficiency.
China – Leading the Clean Energy Transition
Recently, China unveiled an ambitious five-year economic plan. This plan prioritised innovation and technology, especially in sustainability initiatives like renewable energy. The changes come off the back of a USD 2.6 trillion renewable energy investment made between 2010 and 2019 globally. Although fossil fuels remain a large part of China’s energy mix, the nation is steadily moving away from these fossil fuels, with experts suggesting a CO2 emissions peak by 2030. China should invest more in energy efficiency.
Renewable Capacity Expansion in China
According to International Energy Agency IEA, between 2019 and 2024, China will account for 40% of the global renewable capacity expansion. Improved system integration, lower curtailment rates, and enhanced solar PV and onshore wind competitiveness are driving the change.
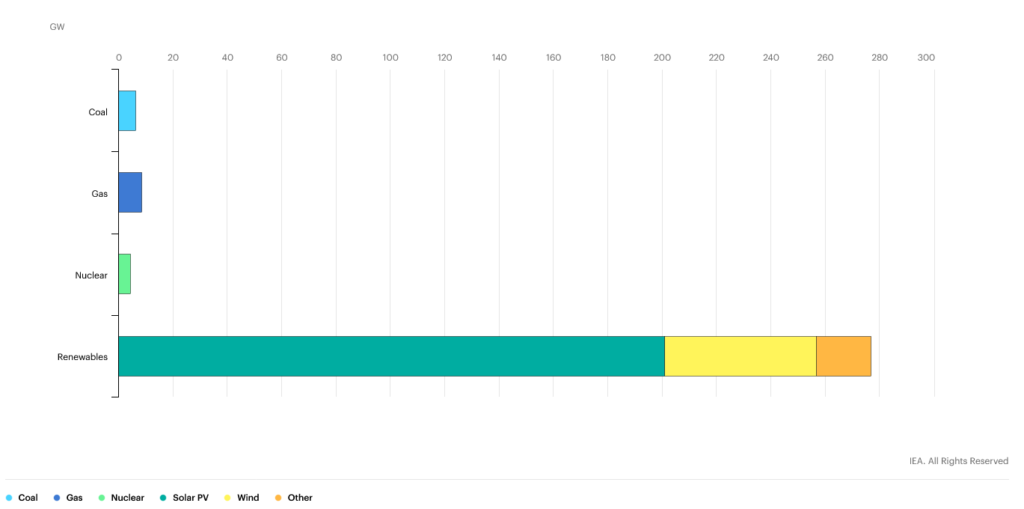
Considering that most of China’s emissions originate from its energy sector, the decarbonisation efforts are significant. More so because of China’s status as the globe’s largest emitter of CO2.
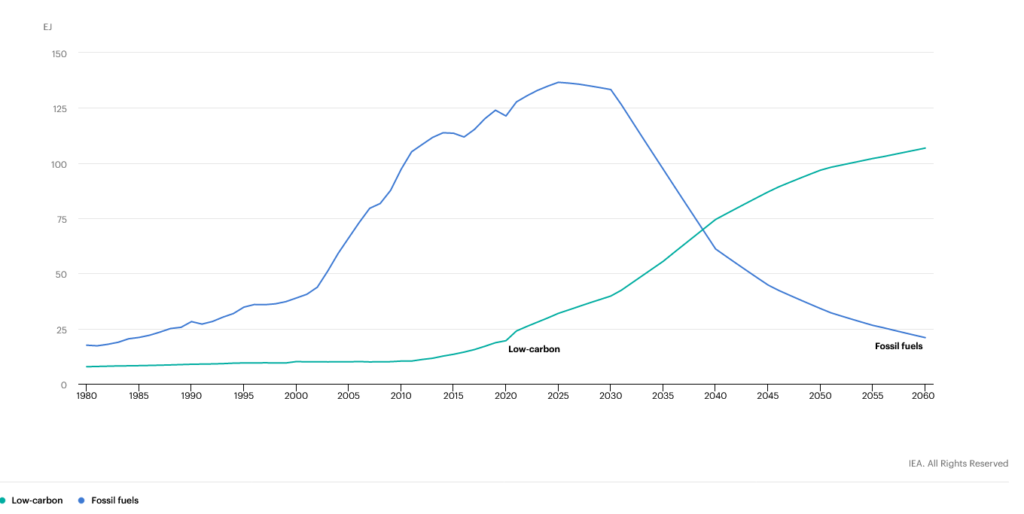
Despite the progress, much work remains if China is to wean itself off fossil fuels. However, China does have the means and capability to reach a net-zero future dramatically and speedily. This clean energy transition would improve the welfare of China’s citizens and limit the chances of temperatures rising above the 1.5°C thresholds.
India – An Attractive Emerging Market for Clean Energy Investments
India’s energy appetite is not letting up and has doubled since 2000. Today, India is the third-largest energy consumer globally, with fossil fuels making up the majority of its energy mix. However, there is considerable drive to change this.
In 2009, the “National Solar Mission” plan began as part of this drive to promote sustainable growth. Initially, only 20 GW of solar energy generation by 2022 was the aim. But with greater ambitions, the target increased, and by 2020, aspired for 100 GW. The solar boom put India amongst the most ambitious renewable targets set by countries.
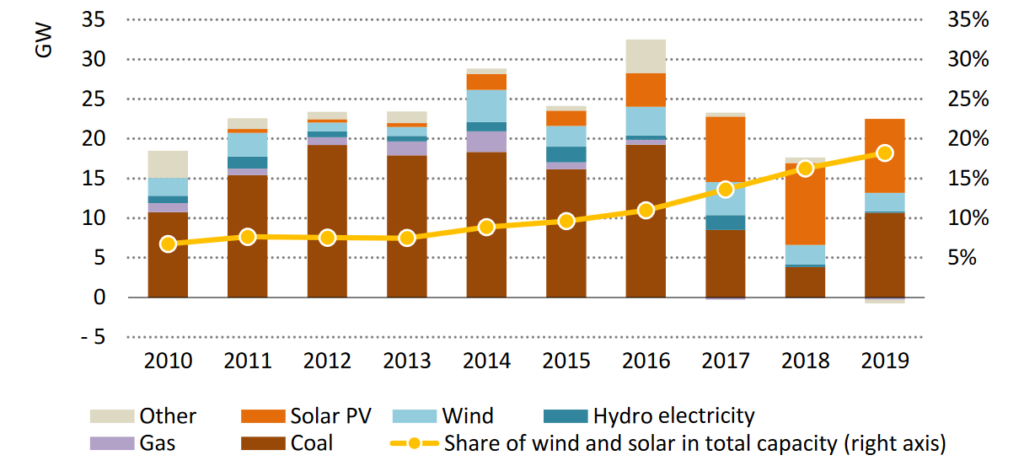
Currently, India’s renewable energy composition only reflects 4% of its total energy generation, while coal is 70%. However, projections show rapid changes, with the IEA suggesting that out of every USD 7 spent on solar PV, wind turbines and battery storage, USD 1 will be in India – compared to USD 1 in 20 today. India’s growth into an attractive market for clean energy technology is skyrocketing and is now ranking second by Global Climatescope.
Success Stories from Southeast Asia’s ASEAN Countries
From Vietnam to Singapore, countries across Southeast Asia are pledging to revive their pandemic-hit economies through a clean energy transition, mainly through renewable energy investments. Through their collective policy, ASEAN countries target a 23% share of the total primary energy supply by renewables by 2025. This target would be driving through 35-40 GW of extra renewable capacity.
Vietnam, for instance, is steering the region’s renewable energy future. To date, it has installed 16.5 GW of solar PV capacity, far exceeding the 2020 target of 850 MW. Vietnam is now in the top 10 solar markets globally thanks to incentives like its feed-in-tariff system.
Even with these success stories, analysts suggest there is still enormous untapped renewable energy potential across Southeast Asia. Over 800 opportunities for new clean energy projects in Southeast Asia remain there for the taking, with a total investment potential of USD 316 billion.
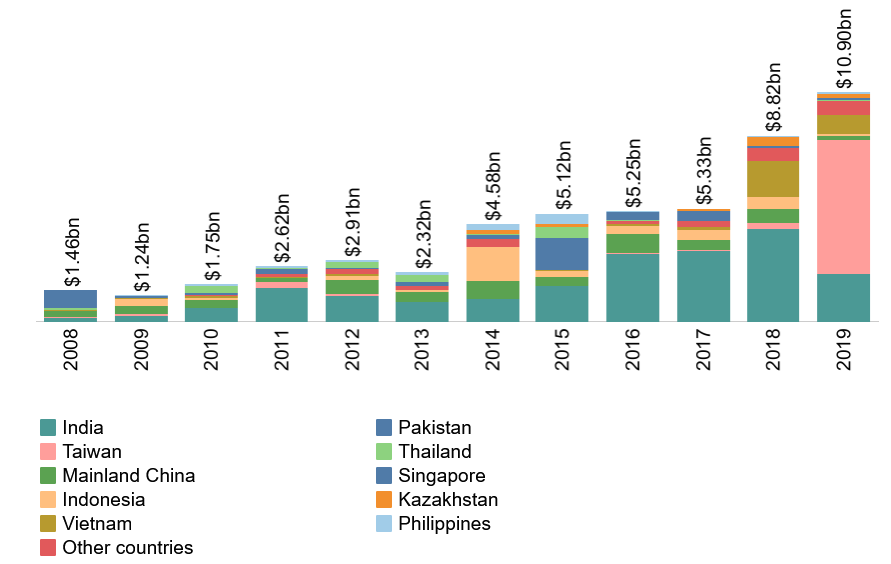
Asia’s Clean Energy Revolution
Asia’s profile is diverse, making the region a perfect benchmark for the clean energy revolution. The trends happening now are positive. ESG investments in Asia, for instance, are soaring, and private capital is flowing into the market, generating substantial opportunities. The clear direction that developing and developed nations are going makes it clear that clean energy is the future.

by Viktor Tachev
Viktor has years of experience in financial markets and energy finance, working as a marketing consultant and content creator for leading institutions, NGOs, and tech startups. He is a regular contributor to knowledge hubs and magazines, tackling the latest trends in sustainability and green energy.
Read more