Facts About Gas Create A Divide In Its Future
Avigator Fortuner / Shutterstock.com
19 January 2023 – by Eric Koons
Gas Facts – Overview
Many facts about gas provide an argument for its role as a transition fuel in the global energy transition. First, despite being a carbon-based fuel, natural gas produces significantly fewer emissions than its common fossil fuel peers, oil and coal. This fact about natural gas and its flexible nature are why it generates 25% of the world’s electricity. Natural gas industry is flourishing due to this fact.
However, it is still a fossil fuel and only produces 50% less carbon dioxide than coal. Relying on natural gas for energy is not a solution to climate change and may slow the renewable energy transition.
What Is Natural Gas?
Natural gas is a hydrocarbon-based fuel with a high energy density that can be transferred, stored and used in liquid and gas forms.
When Was Gas first Used?
Thanks to these characteristics, popularity of gas is increasing, but it has been around for a long time. One of the first recorded uses was for boiling water in China in 500 BC.
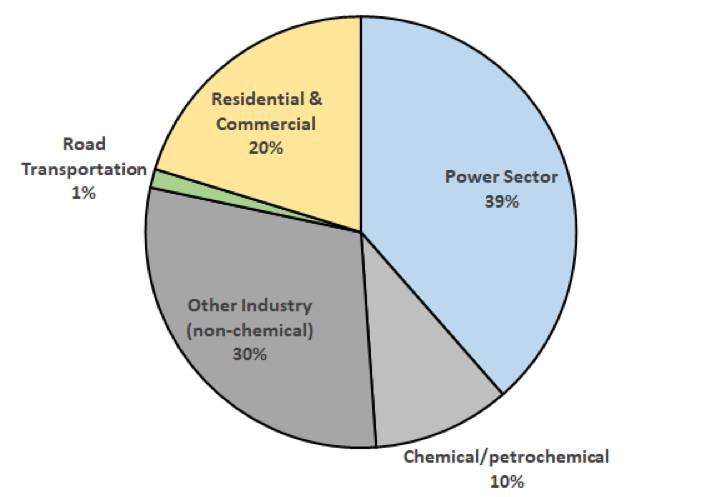
Primary Use of Gas
The primary use of gas is for electricity, but its use is growing for heating, transportation and manufacturing.
The production of petrochemicals, such as plastic and fertiliser, heavily relies on natural gas and will continue to take more share of global production in the coming years. The International Energy Association (IEA) estimates that petrochemicals will require an additional 56 billion cubic metres of natural gas by 2030.
5 Interesting Facts About Gas
Natural gas is becoming so widespread that as many as 58 million homes in the US use natural gas for heating and cooking. This results from natural gas’ reputation as a cheap, reliable and comfortable energy source. Here are some interesting facts about gas:
1. Methane in Gas
Natural gas predominantly consists of methane (70-90%). While this means there is less carbon dioxide from combustion, methane is also a harmful greenhouse gas. Methane has a global warming potential over 28 times higher than carbon dioxide.
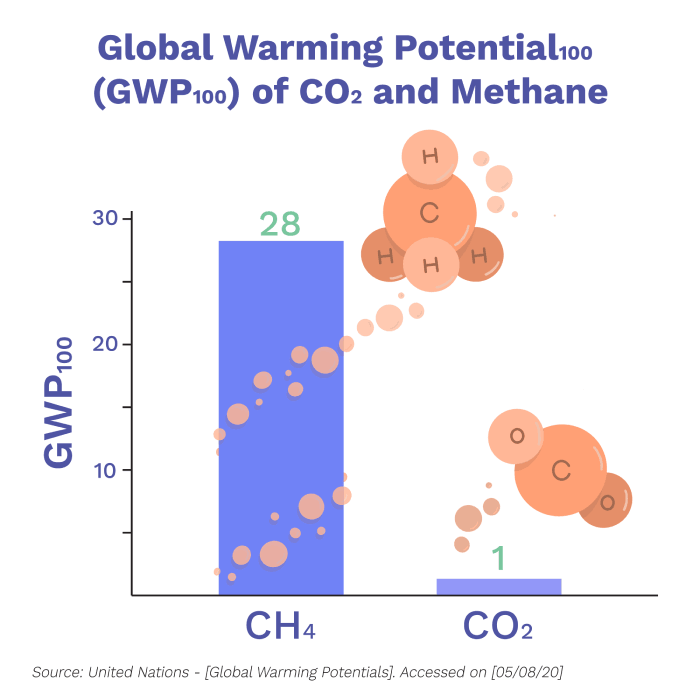
While lower carbon dioxide emissions are important, methane does have a dramatic effect on climate change. This is one of the main arguments that opponents of natural gas hold. It doesn’t stop climate change. It just shifts the type of emissions.
2. Gas as a Transition Fuel
As the world is slowly moving away from fossil fuels, a transition fuel can play an important role in limiting energy emissions in the short term. Natural gas can potentially fill this role and be phased out as renewable energy capacity grows to meet global energy demand completely.
Natural gas fits this picture for a number of reasons:
- It releases less CO2 compared to coal and oil.
- Natural gas is a stable and reliable source of energy.
- It emits less particulate matter.
- The infrastructure for natural gas drilling and distribution already exists.
However, even with these seemingly positive traits, the world may phase out natural gas sooner than previously thought.
The current energy crisis has made the EU change its policies to reduce the dependence on Russian gas, giving way to more renewables. Additionally, this is leading towards natural gas demand destruction, which may permanently limit global natural gas requirements.
3. Natural Gas Compression
Another interesting fact about gas is its space requirements. We capture natural gas as a gas, but the substance is challenging to move long distances. However, with compression and cooling, it can turn into a liquid state.
In this state, natural gas requires 1/600th of the space it does in its gaseous form. As liquid natural gas (LNG), it is easier to ship long distances on tankers specially equipped to maintain the temperature and pressure requirements.
4. Wet Versus Dry Natural Gas
Not all natural gas is equal. Depending on the site of drilling and the contents of the gas, natural gas is wet or dry. Wet natural gas generally contains more water vapour and liquid ethane, propane and butane. Dry natural gas, also called consumer-rate natural gas, has fewer liquids and more methane.

5. Interesting Uses of Natural Gas
Gas is a popular energy source for a variety of reasons. Extraction, storage and transportation infrastructure already exist, so there are fewer new infrastructure requirements than renewables. Additionally, natural gas storage systems are more developed, whereas renewable energy storage needs to be technologically advanced to meet global demand.
Natural gas is used for:
- cooking,
- heating,
- water heating,
- electricity generation,
- transportation,
- materials production,
- manufacturing,
- refrigeration and
- hydrogen production.
The Future of Natural Gas
Many facts about natural gas paint a promising picture for its future in the global energy mix. However, many facts about gas also show that it can damage the long-term transition to renewable energy.
Adopting natural gas as a transition fuel can be viable, but it is a slippery slope. If new infrastructure is built to increase the natural gas supply, it may result in significant rates of stranded assets. As a result, these assets will be costly for companies and governments and may reduce the incentive to transition to renewables fully.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more



