Renewable Energy Companies in Japan Are Crucial For Decarbonisation
Source: The New York Times
09 April 2024 – by Eric Koons Comments (0)
Renewable energy companies in Japan are spearheading the nation’s journey towards a sustainable and green energy transition. The country has set ambitious targets to reduce its carbon footprint and increase the share of renewable energy in its energy mix.
Japan aims to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050, with plans to boost renewable energy to cover 36-38% of its energy needs by 2030. However, achieving these targets has challenges, including technological limitations, financial constraints and geopolitical factors. Additionally, experts are voicing concerns over the untested strategies the country plans to use for decarbonisation, such as clean coal and ammonia co-firing.
That being said, Japan’s renewable energy market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 3.5% over the next decade, led by a mix of public and private sector companies.
What Is Japan’s Main Source of Renewable Energy?
Japan’s renewable energy landscape is diverse, with several existing options. Currently, Japan sources 15.1% of its energy from low-carbon sources. Solar power leads the charge, making up 5.39% of the country’s total annual energy consumption, with hydropower following it at 3.94%. Wind sits at 0.43%, and 2.64% comes from a variety of other renewable sources.
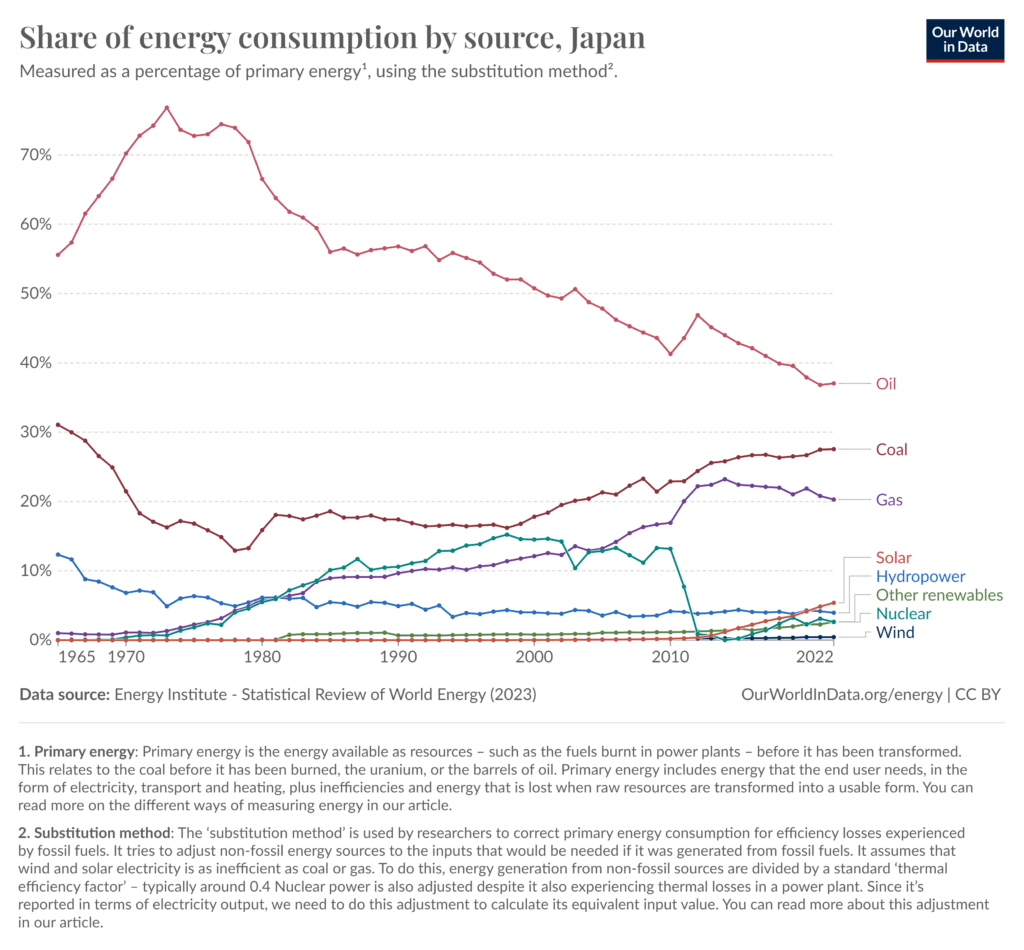
While this is less than half of the country’s 2030 renewable energy target, it’s up from just 5.72% in 2010. This coincides with the Fukushima nuclear meltdown in 2011, which marked a rapid shift away from nuclear power with subsequent investment in renewables. Still, its renewable energy development is lagging behind that of other developed nations.
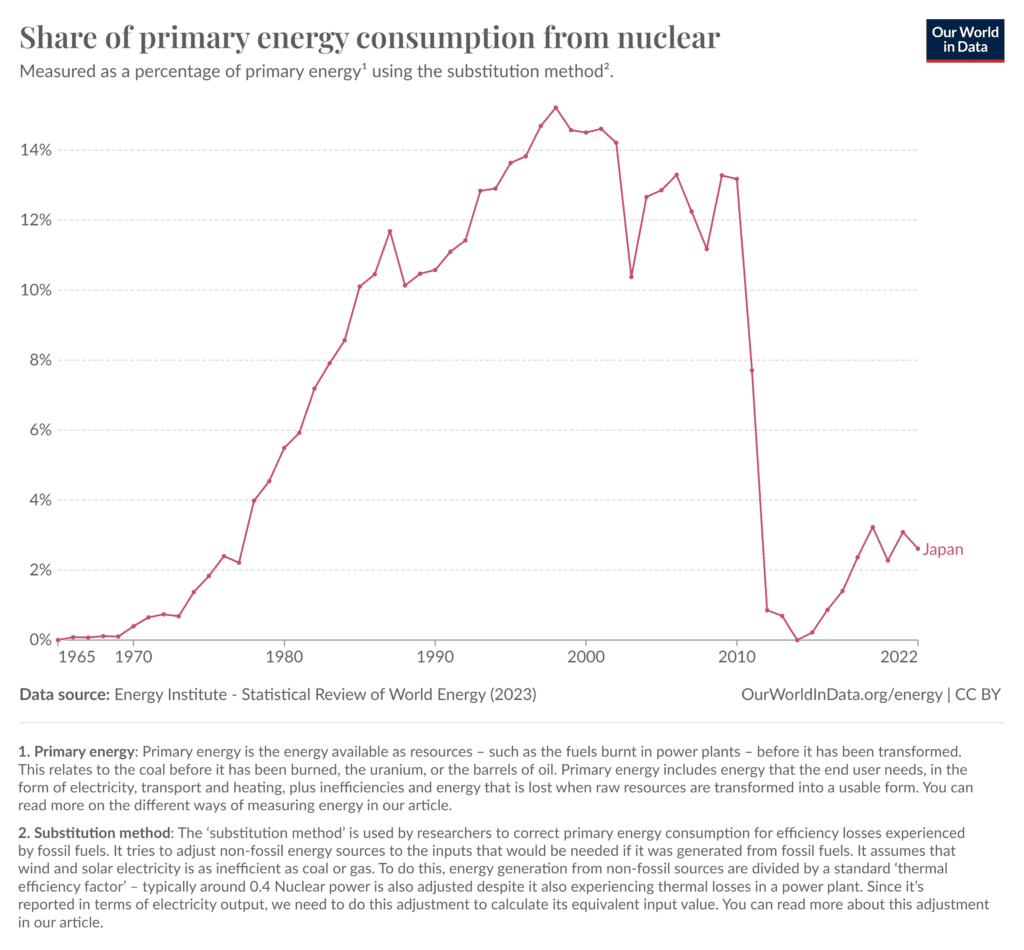
Japan’s Renewable Energy Potential
One of the major concerns Japan has cited with developing solar and wind renewable facilities is its mountainous landscapes and distributed layout of 6,850 islands. This means a majority of land is unsuitable for utility-scale solar facilities, which require relatively flat land. Meanwhile, the grid interconnection between islands is often weak.
However, Japan has vast offshore potential for wind. The estimated offshore wind capacity of the nation is over 9,000 TWh/year, which is more than nine times the country’s projected electricity demand in 2050. Furthermore, the country has barely tapped into its geothermal resources, which are the third largest in the world.
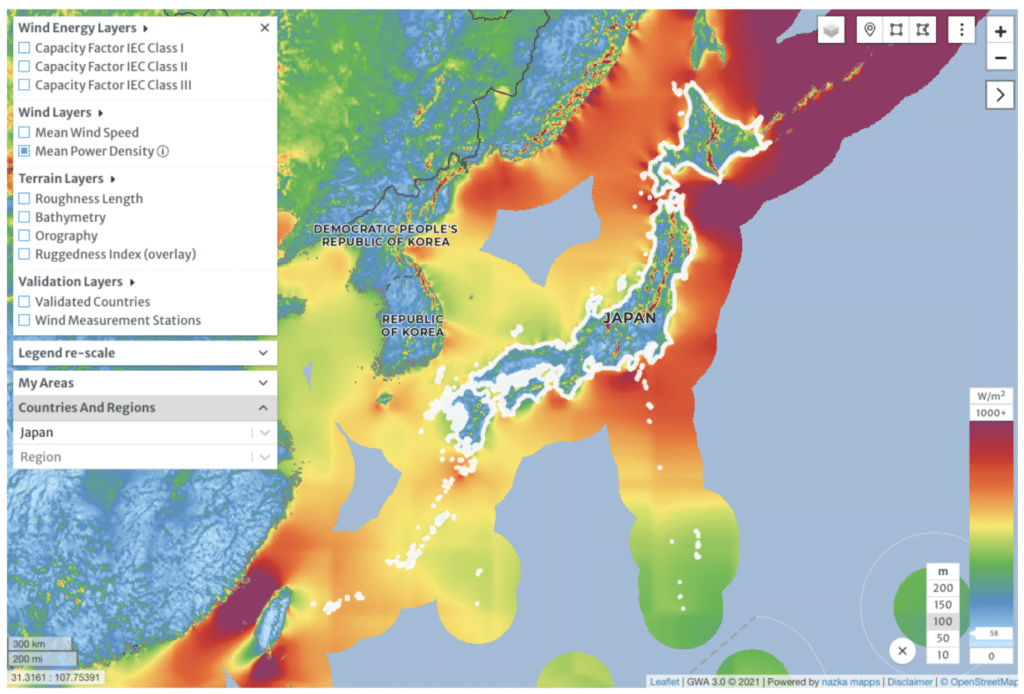
Japan has the potential capacity to run off 100% domestic renewable energy. The nation’s plan to rely on a mix of renewables and questionable low-carbon fossil fuel-based sources is short-sighted. As a result, the country faces growing pressure from ASEAN and G7 nations over its decarbonisation strategy.
Is Japan Investing in Renewable Energy?
These concerns are highlighted by the country’s lagging adoption of renewable energy. However, Japan is increasing its renewable energy investment to meet its 2030 targets. The country will invest more than USD 100 billion in wind and solar before 2030.
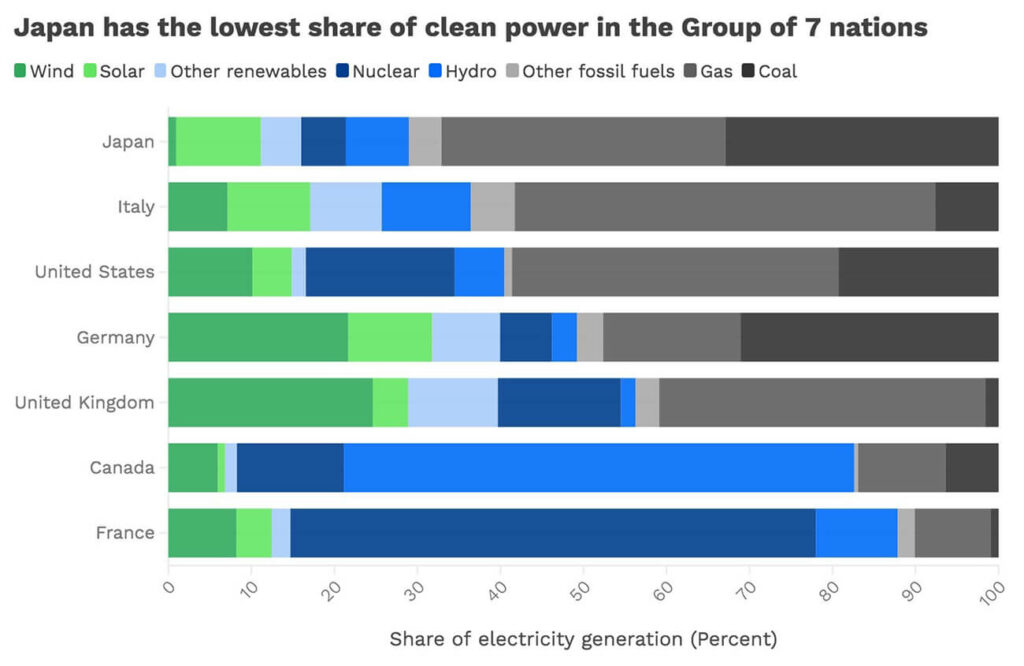
Yet, when the larger energy system is considered, it is clear that this is not nearly enough. Japan spent over USD 1.8 trillion on fossil fuel imports between 2010 and 2022. Furthermore, the country’s 2050 net-zero goal will require an investment of USD 10 trillion by 2050 – around USD 330 billion annually. The stated USD 100 billion investment this decade is just a fraction of what is needed and will place the country further behind in its push for decarbonisation.
The Largest Renewable Energy Companies in Japan in 2024
It is unlikely that the government can fund the needed investment in renewables. This means it will largely fall on the private sector to fill the funding gap. Luckily, Japan’s renewable energy sector is growing and is home to some of the world’s largest energy companies. A few of the most promising Japanese renewable energy companies include the following.
Japan Renewable Energy Corporation
Japan Renewable Energy Corporation (JRE) is one of Japan’s largest renewable-only energy developers. It is a private company that primarily focuses on solar, wind and biomass energy production. The company has an installed capacity of 1.25 GW of renewable energy, with another 113,636 kW under construction. The company owns and operates over 40 solar facilities in Japan and abroad.
JERA
JERA is Japan’s largest fully integrated power generation company, producing 30% of the country’s energy. It is a joint venture between Tokyo Electric Power Company and Chubu Electric Power.
Unlike JRE, JERA is heavily involved in fossil fuel power generation and is the country’s top importer of LNG. However, it also operates some of the country’s largest renewable energy facilities. As of 2022, the company had renewable energy assets with a capacity of 1.2 GW and a stated goal of increasing that to 5 GW by 2025. While this is promising, the company is aiming to be an essential part of Japan’s ammonia and hydrogen co-firing development, which experts see as a roadblock to decarbonisation.
Eurus Energy Group
Eurus Energy Group is an international renewable energy company based in Japan. It is Japan’s largest wind energy developer and has a renewable energy capacity of 1.25 GW in Japan. Globally, it owns 108 renewable energy projects spanning 15 countries and has a total renewable energy capacity of 3.6 GW. It is a partial owner of the Asahikawa Wind Farm, which is Japan’s largest offshore wind facility and the company has 15 other solar and wind projects under construction.
The Road Ahead for Japan’s Renewable Energy Sector
The growth potential for Japan’s renewable energy sector is immense. With the government’s support and strategic investments, the country can overcome the challenges facing its renewable energy goals. Facilitating regulatory reforms, incentivising renewable energy investments and reassessing the country’s decarbonisation strategy can accelerate the transition to a greener energy mix. As Japan continues to invest in renewable resources, the companies leading the charge will be critical in facilitating the necessary sector growth.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more






