Renewable Energy vs Fossil Fuels: A Financial Perspective
Source: Hive Energy
13 February 2025 – by Eric Koons
The choice between renewable energy and fossil fuels is no longer just a buzzworthy topic. It’s a pivotal decision point for business leaders worldwide. With climate change intensifying and energy costs rising, the conversation around clean power has become far more than just virtue signalling. Savvy executives recognise that shifting from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources can significantly bolster both environmental targets and the bottom line.
What Is the Difference Between Renewable Energy and Fossil Fuels?
When we talk about energy sources, we’re essentially discussing where power comes from and how it’s replenished. Renewable energy, including solar power, wind power, hydro and geothermal, relies on natural processes that are continually replenished, such as sunlight or moving water. By contrast, fossil fuels, like coal, oil and natural gas, are formed from organic matter beneath the Earth’s surface over millions of years. Because fossil fuels exist in finite quantities and cannot be easily replaced once extracted, they are inherently unsustainable in the long term.
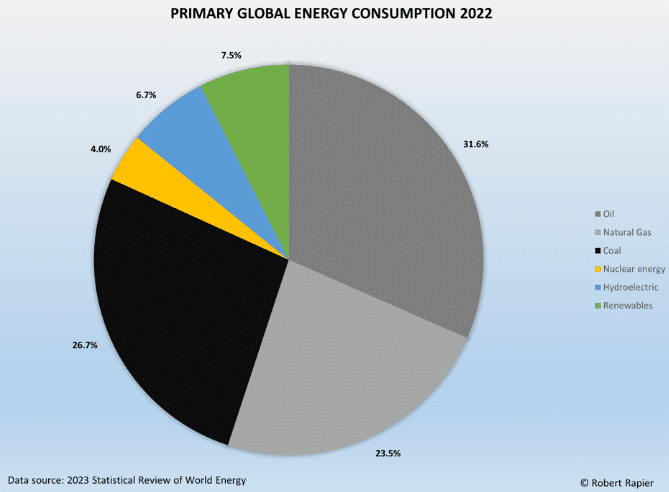
Data from the Energy Institute illustrates that in 2022, fossil fuels still accounted for over 80% of global primary energy consumption, but renewables are steadily increasing their share. This shift is largely driven by concerns over carbon emissions and the looming realisation that fossil fuel reserves won’t last forever.
Is Renewable Energy Better Than Fossil Fuels?
In the debate on renewable energy and fossil fuels, renewables have several advantages:
- Sustainability: Renewable energy resources are infinite because they rely on natural processes that are regularly occurring.
- Lower emissions: Renewables produce nearly zero emissions during operation, and their only source of emissions is from the production of infrastructure, like solar panels. This gives them a much smaller greenhouse gas footprint than fossil fuels. For example, the life-cycle carbon emissions associated with solar electricity is 20 times less than coal.
- Growing affordability: In many parts of the world, renewable energy is already cost-competitive and cheaper than fossil fuels. Additionally, renewable energy technology is rapidly improving, driving costs down further. For example, the cost of solar photovoltaic (PV) electricity declined by 85% between 2010 and 2020.
On the other hand, fossil fuels have dominated for decades, partly due to the following:
- Established infrastructure: Oil and natural gas pipelines, refineries and distribution networks are deeply entrenched worldwide. However, as the world transitions to renewables, this infrastructure may become a stranded asset.
- Reliability: Coal or natural gas power plants can run consistently, regardless of weather fluctuations, whereas solar and wind can be intermittent if not supported by robust energy storage systems.
However, as energy storage technologies rapidly improve and as governments introduce stronger policies favouring green energy, renewables will surpass the existing pros for fossil fuels, eliminating nearly any viable case for fossil fuel energy.
Climate Impact and Business Responsibility
The Earth’s temperature has already risen by more than 1°C since pre-industrial times, primarily due to carbon dioxide emissions from burning fossil fuels. This warming trend increases the frequency of extreme weather events and threatens supply chains, infrastructure and agricultural outputs, factors that significantly concern corporate stakeholders.
At the same time, both consumer demand for environmentally responsible brands and regulatory pressures to meet emissions reduction targets are intensifying. In many regions, companies must now comply with stricter environmental regulations or face fines, public backlash and loss of market share. For instance, China aims for net-zero emissions by 2060, adding urgency to the business case for going green.
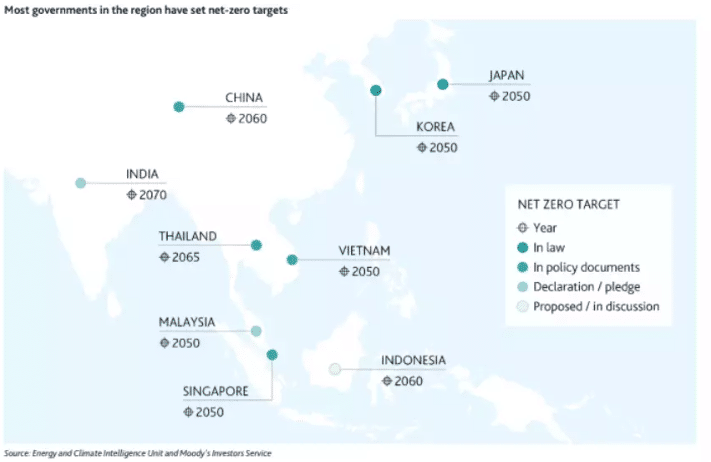
Embracing renewable energy can help companies align with these evolving expectations. Corporations that reduce their carbon footprints benefit not only from a healthier planet but also from positive public perceptions and lower operational costs in the long run.
The Financial Case for Renewable Energy
For many organisations, the conversation boils down to dollars and cents. While installing solar panels or wind turbines can have a high upfront cost, the long-term savings often justify the investment. According to Lazard, the levelised cost of energy (LCOE) for utility-scale solar and onshore wind is now, on average, cheaper than the LCOE for coal, even without government incentives.
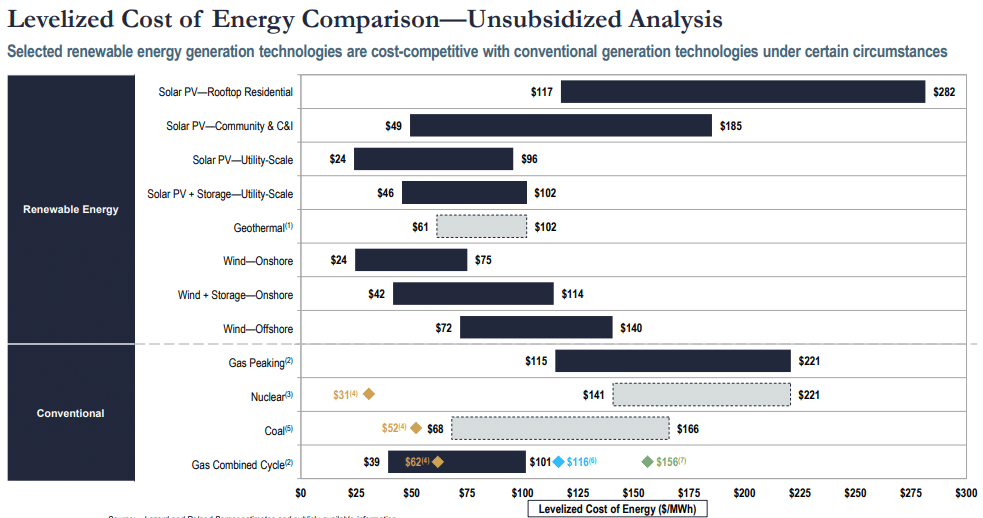
Investing in solar and wind power also provides a hedge against fossil fuel price volatility. Oil and gas markets can swing wildly due to geopolitical tensions and supply disruptions, impacting operational costs. Moreover, looming carbon taxes and stricter emissions trading systems could increase fossil fuel expenses even more.
Government Incentives and Policy Support
Government support continues to make renewables more attractive by lowering financial barriers and reducing the risk of adopting new technologies. In Vietnam, for example, the government offers a range of incentives, such as tax benefits and customs duty exemptions on certain equipment. These measures significantly decrease the initial outlay for businesses, allowing them to invest in clean energy without shouldering prohibitive costs.
Similar or more ambitious schemes exist in other parts of Asia and regions like Germany, where local and federal authorities provide grants or rebates to stimulate the widespread adoption of renewables. In many areas, feed-in tariffs also pay businesses and individuals a fixed rate for any renewable electricity they contribute to the grid. This creates an additional revenue stream, further improving the return on investment.
Embracing Renewables For a Balanced Future
When weighing renewable energy vs fossil fuels, it’s clear the former offers a powerful path forward — not only for climate mitigation but also for securing financial stability. Renewables like solar, wind and hydro are becoming more affordable, reliable and scalable every year, positioning businesses to reduce risk, improve brand image and align with global sustainability goals.
Transitioning away from fossil fuels demands an investment in new technology and thoughtful planning. Yet, as more organisations prove it’s possible to profit while reducing emissions, the question shifts from “Why should we?” to “How soon can we?”
For forward-thinking leaders, embracing renewable energy is an opportunity to drive innovation, fight global warming, safeguard the future of their operations and — ultimately — contribute to a healthier planet for generations to come.
by Eric Koons
Eric is a passionate environmental advocate that believes renewable energy is a key piece in meeting the world’s growing energy demands. He received an environmental science degree from the University of California and has worked to promote environmentally and socially sustainable practices since. Eric’s expertise extends across the environmental field, yet he maintains a strong focus on renewable energy. His work has been featured by leading environmental organizations, such as World Resources Institute and Hitachi ABB Power Grids.
Read more




