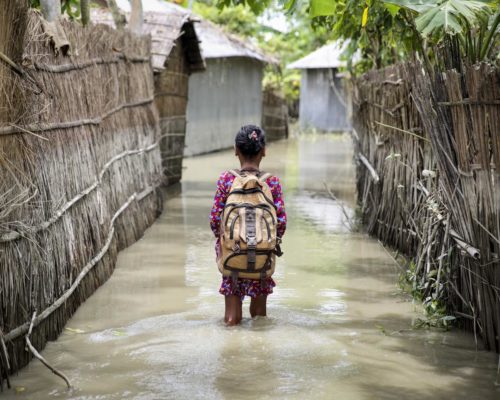
Renewable Energy

Bridging the Gender Gap: The Benefits of Including More Women in Asia’s Energy Sector
Empowering women to participate fully and thrive economically and professionally, especially in the energy sector, is central to a just energy transition. While, globally, there has been progress, albeit slow, Asia stands out as one of the regions where gender inequality in the transition remains most severe.

Top Five Green Energy Stocks in India for 2026
India’s green energy push is scaling rapidly, backed by long-term PPAs, robust grid expansion and strong government support, with a goal of 500 GW in non-fossil capacity by 2030. Foreign capital flow and domestic manufacturing upgrades are fueling a multi-year growth runway in solar, wind and storage, even as tender pace moderates in the near term. Key players such as Adani Green, Suzlon, Waaree Energies, Premier Energies and ACME Solar are well-positioned to benefit from stable cash flows and expanding export opportunities.
Best Renewable Energy Stocks to Buy in 2026
Renewable energy equities are shifting from policy-driven bets to market-driven growth in 2026, with major players delivering contracted cash flows, scalable platforms and AI-powered demand. From NextEra and Brookfield Renewable to solar manufacturers like First Solar and innovators like Nextpower, the sector now blends defensive stability with upside growth as data centres and electrification accelerate demand. This market migration could redefine core portfolios as clean-energy fundamentals align with a multipronged growth thesis.

Best Renewable Energy Companies To Invest In 2026
Investors are shifting capital towards renewable energy as AI, data centres and global electrification drive unprecedented electricity demand. With global renewable investment now surpassing oil and gas by hundreds of billions, companies offering scale, technology and stable cash flows are poised to lead in 2026.
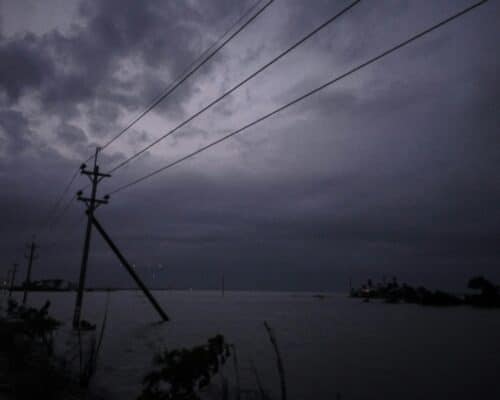

Strengthening Energy Resilience to Overcome Power Outages in Southeast Asia
As extreme weather disasters strike, causing long-lasting outages, disrupting access to essential services and threatening the health of people in affected areas, such events have been common in Southeast Asia recently. The aftermath reminds us of the importance of strengthening the energy system’s resilience. However, in most Asian countries, it remains neglected in climate change adaptation and resilience policies.

Renewable Energy Investment Opportunities in 2026
Renewables have crossed into a mature, capital-driven phase, with solar, wind and hydropower now central to national strategies and grid expansions. Global clean energy investment reached approximately USD 2.2 trillion in 2025, with renewables alone accounting for around USD 780 billion, driven by the increasing adoption of scalable solar and storage technologies as costs decline and long-term contracts become more prevalent. As Asia emerges as the investment epicentre, the energy transition shifts toward infrastructure, grid integration and selective, risk-aware capital deployment.

2026 Renewable Energy Outlook: A Potentially Quieter Year, But Steady Growth to Continue
While most experts anticipate a potentially quieter 2026 for the renewable energy industry, new capacity deployment is expected to continue growing, primarily driven by China. This will ultimately seal the fate of coal power, further accelerating its decline. Still, more ambitious and urgent action is needed to achieve a triple increase in renewable energy capacity by 2030.

Can Renewable Energy Replace Fossil Fuels? What the Data Now Shows
Clean energy is no longer an alternative — it’s becoming the backbone of the global power system. Renewables are overtaking fossil fuels in terms of efficiency, cost and deployment, with solar, wind and storage displacing fossil fuel generation and nuclear gaining momentum, signalling an accelerating transition that reshapes economies, jobs and climate outcomes.

Is Renewable Energy Reliable in a High-demand World?
Renewable energy has transitioned from the fringe to the backbone, with advancements in storage, forecasting and smarter grids enabling the delivery of reliable and cost-effective power. New data show that wind and solar are delivering record shares globally, supported by regional interconnections and long-duration storage that enhance resilience and grid stability.

Renewable Energy Trends 2025: Capacity to Double by 2030
Despite the positive trends, the IEA warns that the COP28 to triple clean energy capacity remains out of reach. To get back on track, countries should minimise policy uncertainties, reduce permitting timelines, increase grid investments and expand flexibility to facilitate the integration of variable renewables and derisk financing.

Is Renewable Energy Expensive? Or Is It the Cheapest Power Source on Earth?
For years, sceptics questioned the cost of renewable energy, but the data now tells a different story. Renewables are not only the cheapest source of new electricity but also the fastest-growing, having decisively outcompeted fossil fuels on price. This surge is driving down energy bills and has led to renewables overtaking coal in the global power mix for the first time.

China’s 2035 NDC: Emissions to Drop 7-10%, Analysts Concerned
There are targets, and then there’s reality, and China’s 2035 NDC perfectly embodies this. While the targets are weak, it is hard to imagine that they weren’t set on purpose, just to be broken afterwards — a habit China has demonstrated over the years.

The Cost of Electricity in Australia: Can Renewables Finally Bring Prices Down?
Australia's energy crisis is deepening, with electricity bills soaring 27% above inflation in just two years. While ageing coal plants and high gas prices are the primary culprits, evidence shows renewables are already helping to curb wholesale costs. The nation's challenge is to accelerate the build-out of renewable infrastructure to secure long-term affordability and stability.

Climate Governance at an All-time High But Challenges Remain
Analysing the progress made in the decade after the Paris Agreement, DDP experts find that climate governance has put us on the right trajectory. However, a lot of work is left, and countries need to scale and accelerate their efforts to avoid the worst impacts of the climate crisis and unlock economic growth and resilience along the way.
Most Popular
Categories
-
10
-
35
-
126
-
4
-
17
-
46
-
52
-
11
-
10
-
15
-
24
-
6
-
1
-
5
-
6
-
286
-
200
-
17
-
24
-
1
-
1
-
23
-
41
-
44
-
88
-
18
-
86
-
43
-
17
-
11
-
43
-
54
-
86
-
299
-
22
-
44
-
36
-
12
-
42
-
36

